In Linux, the “System Monitor” software application is equivalent to a task manager. It shows the running processes, storage consumption details, and system resources. Apart from system monitoring, it also allows the user to stop, end, continue, and kill the processes. The “System Monitor” software application is pre-installed in most Linux distributions.
This guide enlists all possible aspects to locate and use the task manager in Linux.
- Access the Task Manager Via Terminal
- Access the Task Manager Via GUI
- Access the Task Manager Via Shortcut Key
How to Access the Task Manager Via Terminal?
The common line interface allows the Linux user to access and launch the built-in and installed applications easily.
To launch the Task Manager from the terminal, open the terminal and type the “gnome-system-monitor” application name:
$ gnome-system-monitor #For Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora/CentOS/RHEL(gnome-desktop)
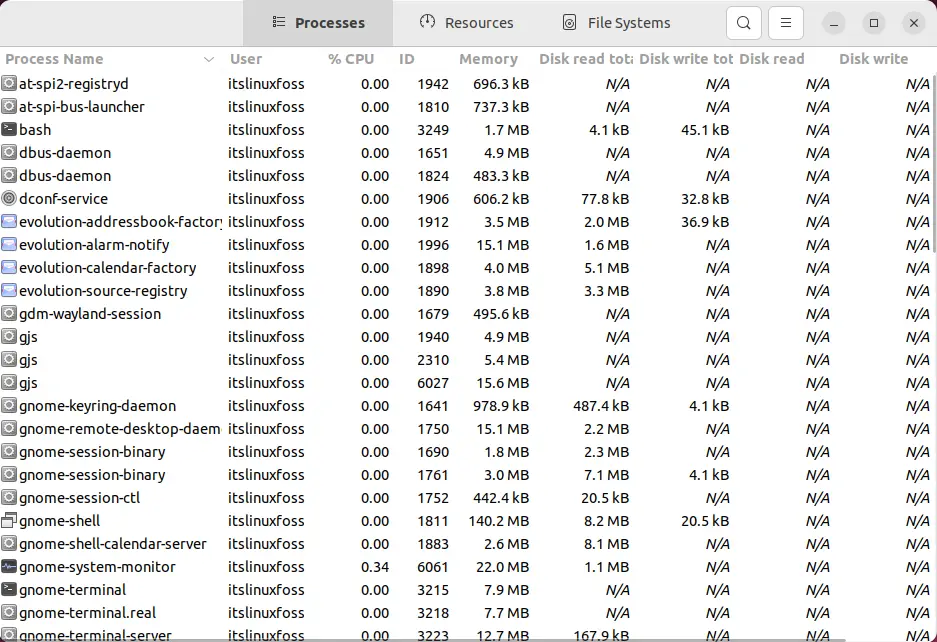
The “gnome-system-monitor” tool is opened.
How to Access the Task Manager Via GUI?
The GUI method is also simple and straightforward to access the “System Monitor” tool in Linux.
Open the “Application Menu” and search for the “System Monitor” application using the “Search” bar. Click on the shown result:
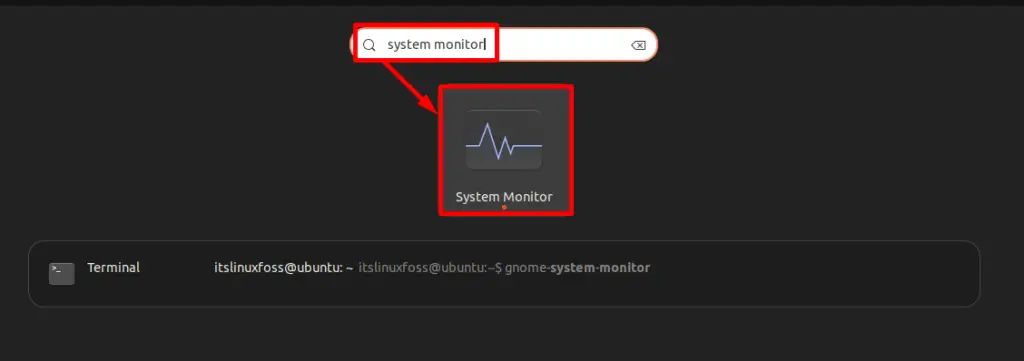
The interface of the “System Monitor” will be opened instantly:
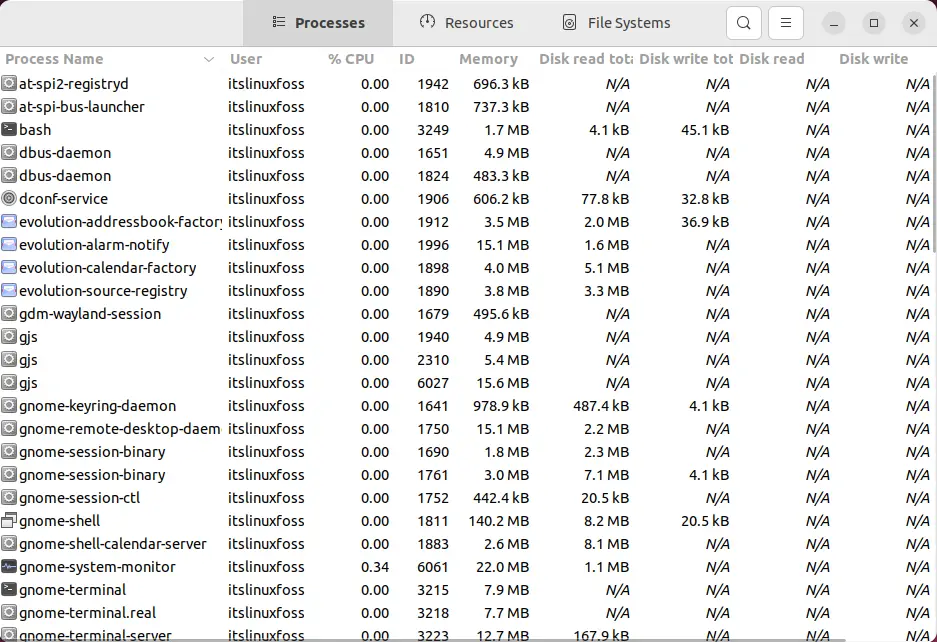
Alternative: How to Access the Task Manager Via Shortcut Key?
In Windows, the task manager is opened by pressing the shortcut “Ctrl+Alt+Del”. However, in the Linux GNOME desktop environment, this key is used to log out of the system.
In order to set this shortcut key, read our detailed article “Launch Task Manager on Ubuntu Via “Ctrl+Alt+Del” ?”.
Conclusion
The Linux distributions that support the gnome-desktop environment come with the “System Monitor” tool as a task manager by default. It can be easily accessed through the “Command Line”, “Graphical User Interface”, and the most convenient method, the “Ctrl+Alt+Del” shortcut key. This guide has illustrated all possible aspects of accessing the task manager on Linux.
