In Linux, the /var/www directory stores web content for the Linux server. Most of the server’s default settings are configured to always look for the content in the “/var/www” directory. Only the root has 777 (read, write, and execute permissions). There may also be a need to give other users these permissions at some point.
This guide will present how the “777” permissions can be applied on the subdirectories of “/var/www.”
- What is 777 in Linux?
- How to chmod 777 on all Subfolders of /var/www?
- Why should you not Grant 777?
- Revoke chmod 777 on all Subfolders of /var/www?
What is 777 in Linux?
The Linux system controls file/directory access through the permissions set by the owner/administrator. To grant these permissions, the chmod command is there. The 777 means granting all permissions (Read, Write, and Execute) to all users (owners, groups, and others).
Here is a table showing the permissions (777).
| Permissions | Read | Write | Execute | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| Groups | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| Others | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
A detailed guide about 777 in Linux can be read here.
chmod 777 All Subfolders of /var/www
The chmod command, when used with the “R” flag (recursive), grants read, write, and execute (777) permissions to all users. The following command applies the “777” permissions on the “/var/www” in the following manner:
- “Chmod” is executed with the sudo privileges.
- -R stands for recursive (applies on all directories/subdirectories).
- 777 are the permissions (read, write, and execute) to all users (owner, groups, and others).
- /var/www is the directory where the whole command is applied.
$ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www
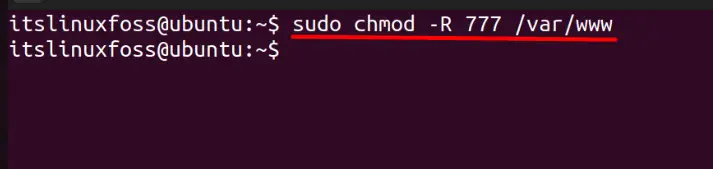
The above command modifies the permissions of the “/var/www” directory.
To check permissions of /var/www, use this command:
$ ls -l /var/www
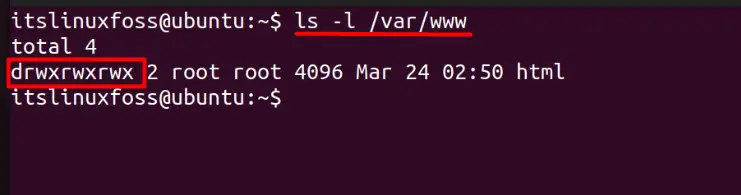
Here is the breakdown of the above output:
- total 4 is the number of directories.
- In the following line, the d stands for the directory.
- After d, there is a set of permissions.
- rwx is Read Write Execute.
- rwx is the read, write and execute permissions for the owner.
- The second rwx is the group’s read, write and execute permissions.
- Thord rwx shows the read, write and execute permissions for others (users).
Why Should you not Grant 777?
By giving 777 to a folder, especially the /var/www, most of the Linux security privileges are bypassed. If these permissions are granted, anyone with access to the system can read, write, and manipulate essential data.
It leaves the files/folders unprotected, and the server security is compromised, which is the last thing you want.
How to Revoke chmod 777 on All Subfolders of /var/www?
If you are unsatisfied with the security threats that chmod 777 on your server, then use this command to revoke chmod 777 on all subfolders of /var/www:
$ sudo chmod -R 700 /var/www
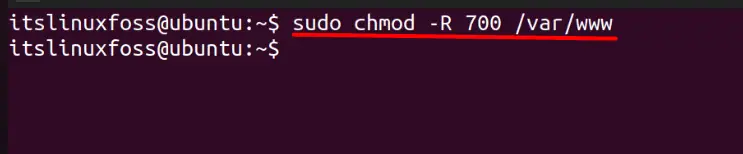
And now only root can access and manipulate the /var/www directory which can be confirmed using this command:
$ sudo ls -l
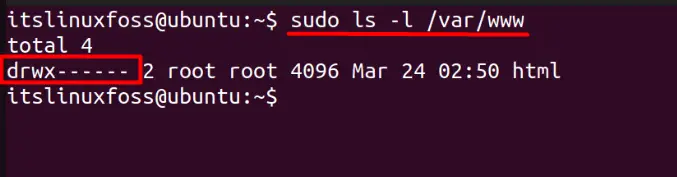
As seen above, the “sudo” is used because all the permissions are revoked, and only the owner (root) can read, write, and execute in /var/www directory.
Conclusion
The chmod 777 grants all permissions to all users on the system, and the same is applied to /var/www. It is quite a vital directory as it is where all the contents of the web servers are stored. As explained, the chmod 777 to /var/www is not considered a good practice because of the security threats.
This guide sheds light on how to chmod all subfolders of /var/www and why you should not do it.

TUTORIALS ON LINUX, PROGRAMMING & TECHNOLOGY