Network File Server commonly known as the NFS is the mechanism to share files between the host and client. Unlike nowadays, it has not been possible to share the hard disk of computers with other computers since some years back.
NFS provides ease to the users to share files and directories using the network communication to remote computers. Using the NFS server, the users can set a specific computer as the host machine and then access it for storing the files.
This blog will describe the installation and configuration NFS servers on Debian 12. For a better understanding, the usage of the NFS server will also be demonstrated by connecting with the client machine. The outline of this post will be shown below:
- What are the Installation Steps for NFS Server on Debian
- What are the Configuration Steps for NFS Server on Debian
- What is the Usage of the NFS Server on Debian
- How to Uninstall NFS Server on Debian
Let’s start the post with the installation of the NFS Server on Debian 12.
What are the Installation Steps for NFS Server on Debian?
The NFS server package is available in the Debian default repository. Once all the packages are updated, it can be installed using the default package manager that is the apt command utility. Follow procedures explained in the next mentioned steps for the installation of NFS Server on Debian.
Step 1: Open the Terminal and Update Packages
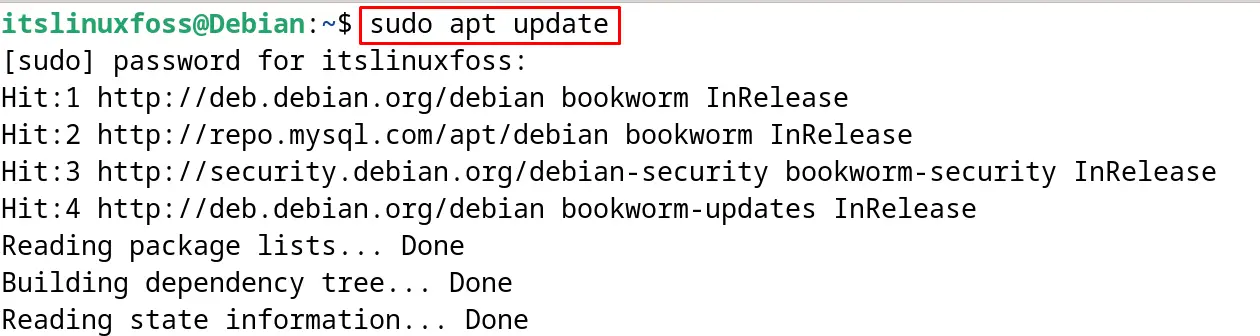
First, launch the terminal and use the “update” option of the apt command to update all the packages:
$ sudo apt update
Step 2: Install NFS Server on Debian 12
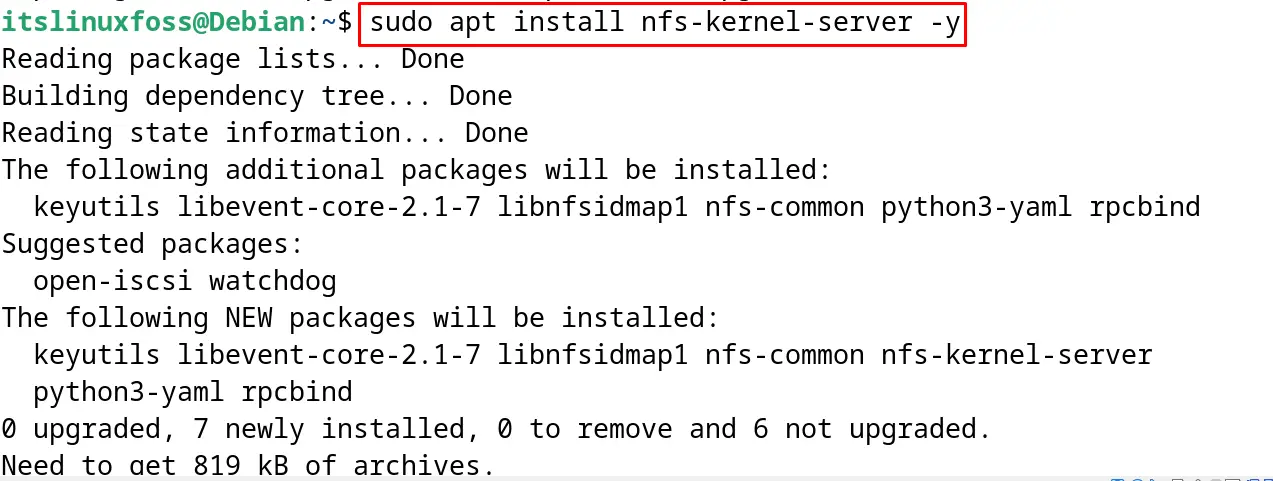
Install the NFS Server on Debian 12 with the execution of the command:
$ sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server -y
Step 3: Start the NFS Server
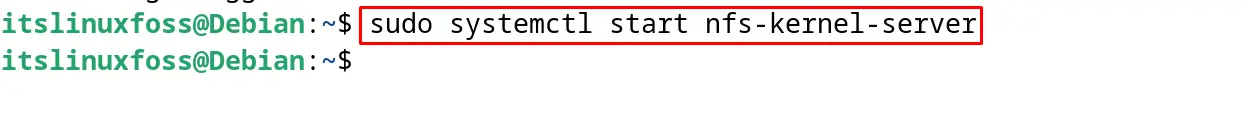
To start the service of the NFS, run the command:
$ sudo systemctl start nfs-kernel-server
Step 4: Enable the NFS Server
To make sure the NFS server should start at bootup, enable it with the systemctl command:
$ sudo systemctl enable nfs-kernel-server

Step 5: Display the Status of NFS Server
After starting and enabling the NFS server, display its status by running the command:
$ sudo systemctl status nfs-kernel-server
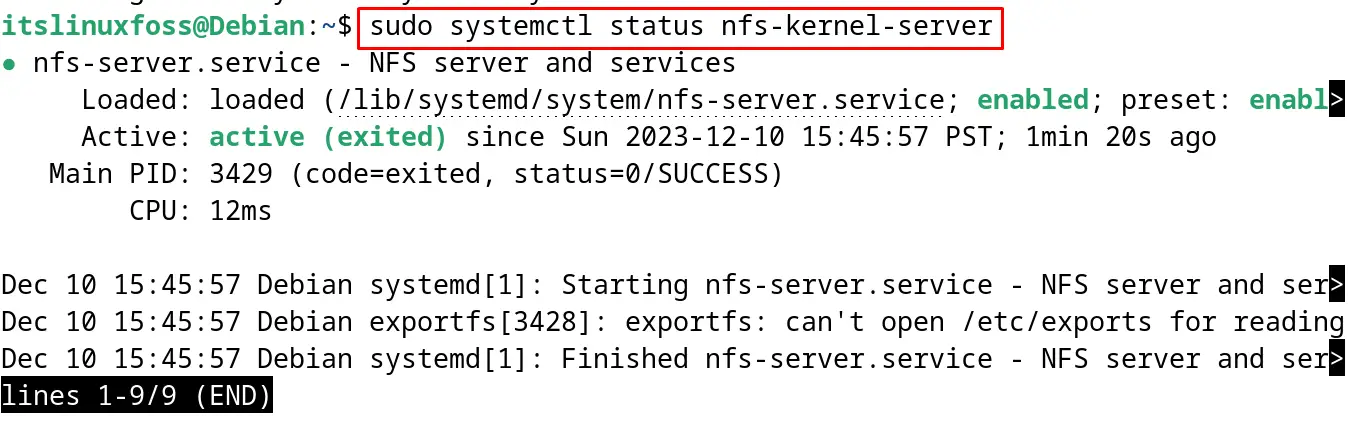
The output displays the active status of the NFS server which also confirms that it has been successfully installed on Debian 12.
What are the Configuration Steps for NFS Server on Debian?
After the installation of the NFS server, it’s time to configure the NFS server with the steps explained next.
Step 1: Create a Directory
First, create a parent directory in the /mnt/ directory where the client machines can store files and directories. This can be done with the “p” option of the mkdir command with a unique name for the directory:
$ sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ItsLinuxFoss_NFS_Server

The successful execution of the above command ensures the creation of the “ItsLinuxFoss_NFS_Server”.
Step 2: Change the Ownership
To change the ownership of the newly created directory to “nobody”, run the command:
$ sudo chown -R nobody:nogroup /mnt/ItsLinuxFoss_NFS_Server/

Step 3: Accessibility of the Directory
The directory created in the above steps will be used by the server’s users to store and share their files. To make the directory accessible to every user of the server, run the command:
$ sudo chmod 777 /mnt/ItsLinuxFoss_NFS_Server/

Step 4: Update the export File
Now update the /etc/export file such that the NFS server gets familiar with the newly created directory, for instance, open the export file:
$ sudo nano /etc/exports

Now add the below-mentioned line at the end of the file by replacing the IP address of the client machine:
/mnt/ItsLinuxFoss_NFS_Server 192.168.139.62/24(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)
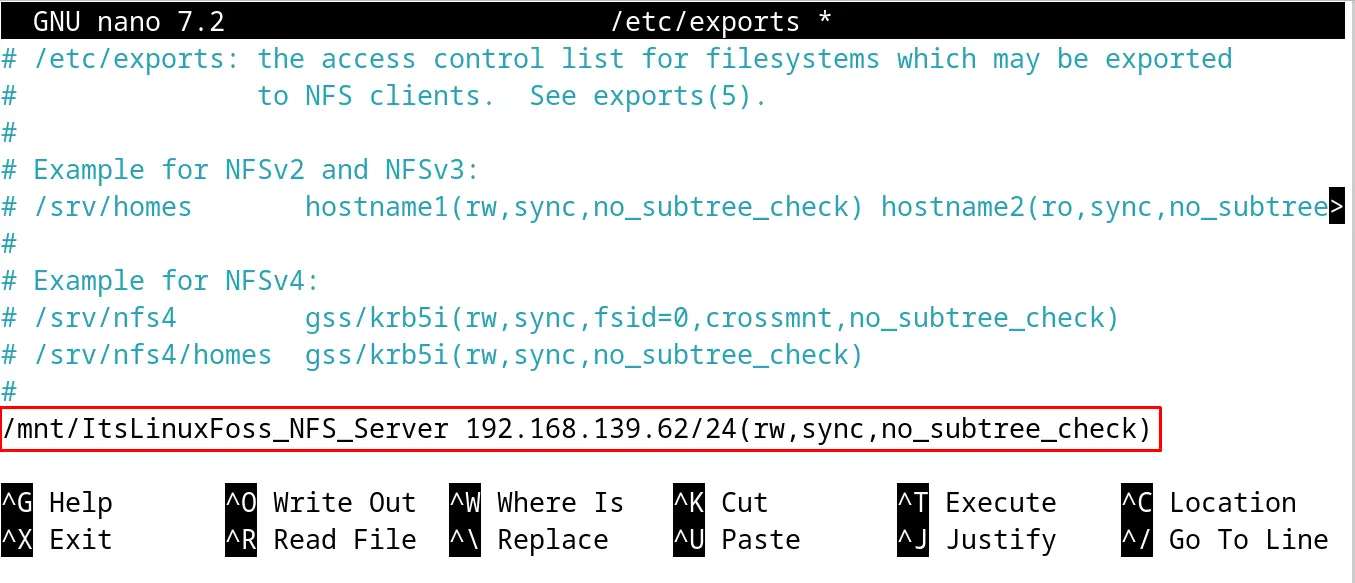
This will mount the subnet of the client machine with the following things:
- the “rw” will grant the read and write permissions to the added client machine
- Changes in the data will be synchronized on an immediate basis with the “sync” option
- To optimize the performance of the NFS server, the subtree check has been disabled
Close the file by saving the changes and to apply the new changes made in the export file, export it using the command:
$ sudo exportfs -a

The successful execution of the command validates the successful configuration of the NFS Server.
Step 5: Reload the Service
Restart the NFS server to save and apply the new changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server

Step 6: Configure UFW
To allow the network traffic of the NFS server, enable the installed UFW:
$ sudo ufw enable

Now allow the specific IP address to connect with the machine to interact with the NFS server:
$ sudo ufw allow from 192.168.139.62/24 to any port nfs

Finally, display the status of UFW:
$ sudo ufw status
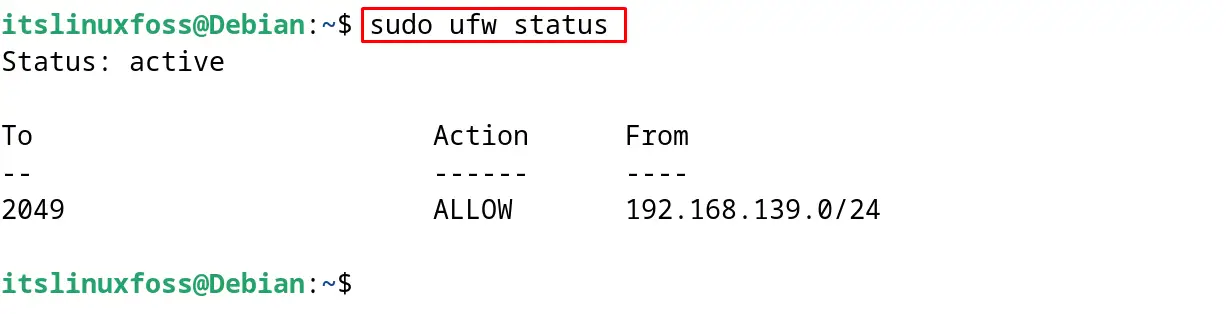
The configuration of the NFS server has been completed. Now it’s time to connect the client machine with the NFS server.
What is the Usage of the NFS Server on Debian?
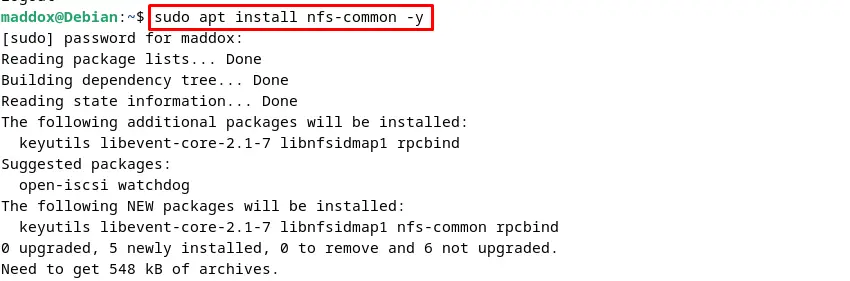
To access the NFS server, first install the NFS Server on the client machine:
$ sudo apt install nfs-common -y
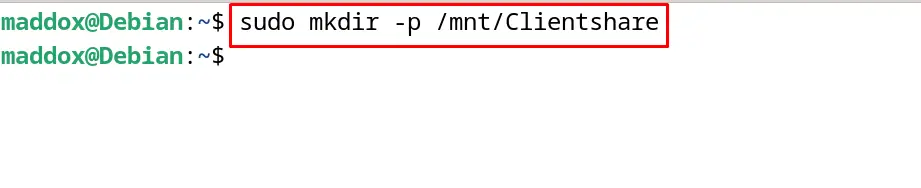
Now create a directory in the client machine to mount it with the NFS server in the next step:
$ sudo mkdir -p /mnt/Clientshare
Mount this directory with the shared file of the NFS server to access it:
$ sudo mount 192.168.139.120:/mnt/ItsLinuxFoss_NFS_Server /mnt/Clientshare

Finally, display the contents of the NFS server from the client machine:
$ ls -l /mnt/Clientshare/
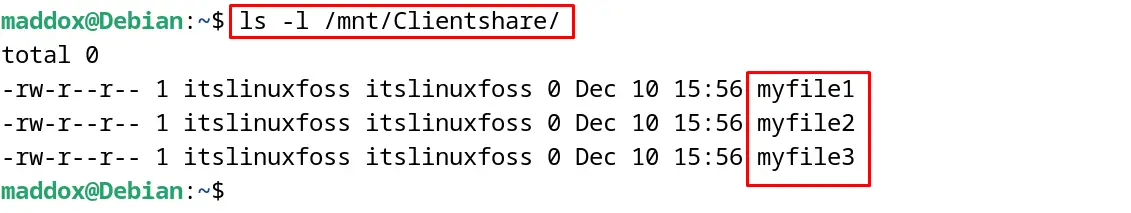
The content of the Clientshare has been displayed on the screen.
How to Uninstall NFS Server on Debian?
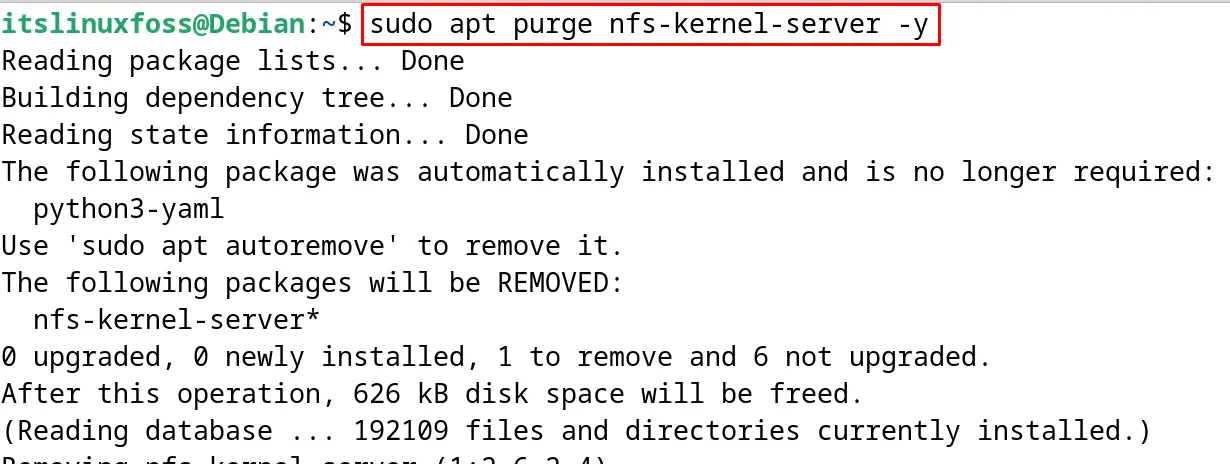
If users want to uninstall the NFS Server on Debian, then use the apt command’s purge option. This will uninstall the NFS Server on Debian along with the removal of all its files:
$ sudo apt purge nfs-kernel-server -y
This is all about the installation, configuration, and usage of the NFS Server on Debian.
Conclusion
In order to install the NFS server on Debian 12, type the command “sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server -y” in the terminal and execute it. When the installation is completed, configure the NFS server by adding the information of the client machine in it.
The step-by-step guide for the installation and configuration of the NFS Server has been demonstrated in this post. Also, the usage has been explained by connecting the client machine with the NFS server. Lastly, the uninstallation step has also been demonstrated on Debian.
