In Python, a Dataframe is a 2-dimensional representation of data in the form of rows and columns. Python provides a Pandas library that can be used to access the Dataframe. Inside that Pandas library, a function named “dataframe.isin()” is utilized that especially checks or filters the specific data.
This write-up will give you an in-depth understanding of Pandas “dataframe.isin()function with numerous examples. This Python guide covers the following topics:
- What is Pandas DataFrame isin() Function?
- Example 1: Check the Specified Value Using Pandas dataframe.isin()
- Example 2: Comparing the Value of One DataFrame With Another Using Pandas dataframe.isin()
- Example 3: Checking the Dictionary Value in DataFrame Using Pandas dataframe.isin()
Let’s start the guide!
What is Pandas DataFrame isin() Function?
In Python, the pandas “dataframe.isin()” function is used to check whether the data frame contains the specified value. By doing so, the data can be filtered effectively. The syntax of the Pandas “dataframe.isin()” function is shown below:
Syntax:
dataframe.isin(values)
In the above syntax, the parameter “values” takes any iterable, series, DataFrame, or dictionary. The “dataframe.isin()” function returns true or false for the respective values of the Dataframe, as it replaces the boolean value in the original Dataframe.
Let’s have a look at the examples given below to implement this function practically.
Example 1: Check the Specified Value Using Pandas dataframe.isin()
In the example given below, the “dataframe.isin()” function is used along with“range()” iterable to check the specified value in the data frame.
Code:
import pandas as pd
#create dataframe
dataframe = pd.DataFrame({'Name': ['Alex','Lily'],'Position': [1, 5], 'Marks': [55, 70]})
#check the data frame marks are in the range(50,60)
result = dataframe.isin(range(1,60))
print('DataFrame\n',dataframe)
print('\nDataFrame are present in range: \n',result)
In the above code:
- The “pandas” library is imported as “pd”.
- The “pd.DatafFame()” is used to create a Dataframe with column names “Name”, “Position” and “Marks”. All the columns contain two values, each at index “0” and “1”.
- The “dataframe.isin()” function accepts the “range()” iterable as an argument.
- The range values of the Data Frame will be compared with the range specified i.e. (1, 60). It will embed true or false instead of the original values of the Dataframe.
- It retrieves the boolean value “True” if the data frame contains a range-specific value.
Output:
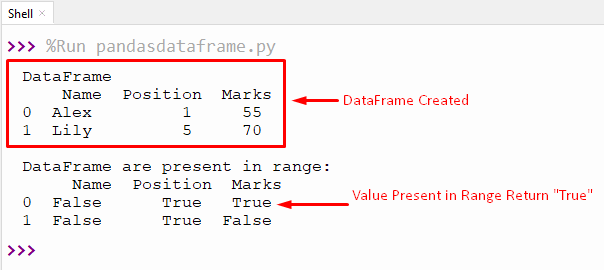
First, a data frame is created, and then each element of the data frame is checked by the range value using the “dataframe.isin()” function.
Example 2: Comparing the Value of One DataFrame With Another Using Pandas dataframe.isin()
In the example given below, the “dataframe.isin()” function checks the value of one data frame with another.
Code:
import pandas as pd
#create first dataframe
first_dataframe = pd.DataFrame({'a': [1, 3], 'b': ['Alex', 10]})
#create second dataframe
second_dataframe = pd.DataFrame({'a': [2, 3], 'b': ['Alex', 3]})
result = first_dataframe.isin(second_dataframe)
print('First DataFrame: \n',first_dataframe)
print('\nSecond DataFrame: \n',second_dataframe)
print('\nChecking Value of DataFrame:\n',result)
In the above code:
- The “pandas” library is imported as “pd”.
- The “pd.DataFrame()” is used to create two data frames and stored in variables named “first_dataframe” and “second_dataframe”.
- The “first_dataframe.isin()” takes the value of the second data frame as an argument and returns the boolean value “True” if elements are matched else, “False”.
- By using this function, all the elements of one data frame can be easily filtered out.
Output:
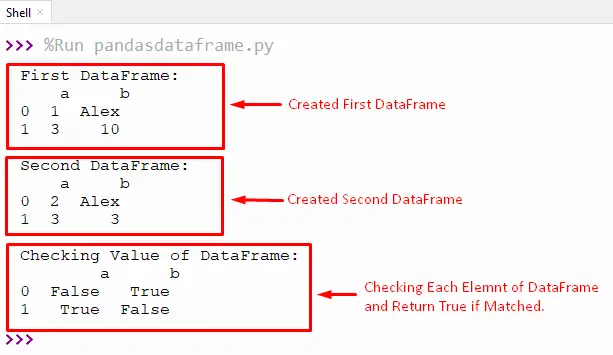
This output returns true if the data frame element is matched. Otherwise, it returns false.
Example 3: Checking the Dictionary Value in DataFrame Using Pandas dataframe.isin()
In the code given below, the pandas “dataframe.isin()” function checks the contained value of the dictionary in the given data frame.
Code:
import pandas as pd
#create dataframe
dataframe = pd.DataFrame({'Name': ['Alex','Lily'],'Position': [1, 5], 'Marks': [55, 70]})
#create dictionary
dictionary = {'Position': [1, 5]}
#DataFrame.isin(dict)
result = dataframe.isin(dictionary)
print('DataFrame Value: \n',dataframe)
print('\nDictionary Value: \n',dictionary)
print('\nChecking Dictionary Value in DataFrame: \n',result)
In the above code:
- A Dataframe is created and stored in a variable named “dataframe”.
- The dictionary value is initialized with the same key name also present in the given “DataFrame”.
- The “dataframe.isin()” function takes the value of “dictionary” as an argument and matches each element value of the data frame. If the element value of the dictionary is matched, then this function returns a “True” value.
Output:
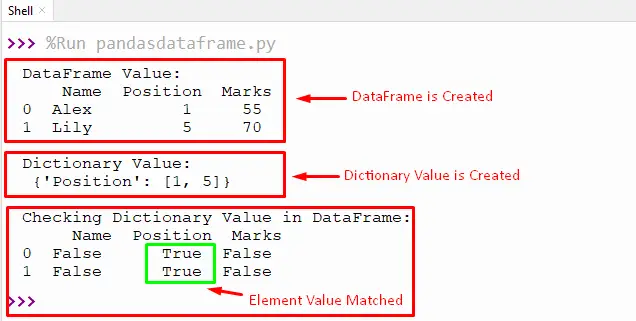
In the above output, the Dataframe containing the dictionary value returns the “True” value using “dataframe.isin()” function.
Note: The “isin()” function is also used to check the other iterable objects, such as list, series, tuple, etc., in the given data frame using the same method.
The guide is now complete!
Conclusion
In Python, the function “dataframe.isin()” is used to determine whether every element/item in a data frame is included in a value. The values can be a list, dictionary, Dataframe, series, range, etc. The “dataframe.isin()” takes the value as an argument and returns “True” or “False” if each element is found in the data frame or not. In this guide, we take “dictionary”, “range”, and “data frame” as an argument in the “dataframe.isin()” function and check the contained value in the given data frame.
This python guide covered pandas’ “dataframe.isin()” function in detail with multiple examples.
