The PWD is a short form of “Print/Present Working Directory” that is used to print the absolute path of the current directory. In most Linux distros, you may get a hint of the current directory from the terminal. However, this “pwd” utility is quite useful, especially when you do not have any hint about the exact path of the directory. Considering its importance, this guide will demonstrate the working and usage of the “pwd” command with various examples in Linux.
The content carried out by this guideline is as follows:
- How Does pwd Command Work?
- How to Use the pwd Command in Linux?
- Example 1: Find the Path of the Working Directory
- Example 2: Print Physical Directory
- Example 3: Print the Value of $PWD
Let’s start this article.
How Does pwd Command Work?
Most network administrators use the “pwd” command to invoke the complete path of the current or previous active (working) directory. The syntax of the “pwd” command is stated below:
Syntax:
$ pwd <options>
Options:
Different options for the “pwd” command are explained as below:
| options | Description |
| -p (physical) | This option refers to the actual path. |
| -l (logical) | It prints out the symbolic path. |
| -v (version) | It represents the current version of pwd |
| –help | It displays all the helpful information regarding pwd. |
To explore more about the “pwd” command, the “pwd –help” can be used as follows:
$ pwd --help
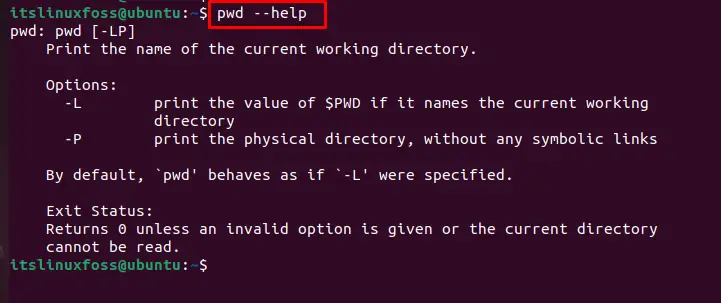
Let’s explore the usage of the pwd command.
How to Use the pwd Command in Linux?
The “pwd” command has various practical usages, including physical and symbolic addresses. Different examples of “pwd” commands are explained here:
Example 1: Find the Path of the Working Directory
The primary usage of the “pwd” command can be accessed via the following command:
$ pwd
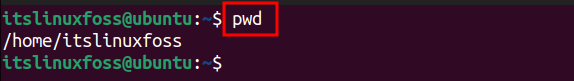
After executing the command, you can display that current directory is “home”.
Example 2: Print Physical Directory
The physical path of the present directory can be obtained through the “-P” option of the “pwd” utility as follows:
$ pwd - P
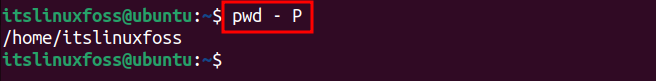
It also prints the address of the present directory.
Example 3: Print the Value of $PWD
By default, the “$PWD” variable points towards the path of the current directory. Its value can be retrieved using the “-L” option of the “pwd” command as described below:
$ pwd - L
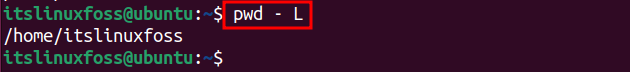
Let’s dig into some more usage of the “pwd” utility.
How to Use pwd Command in Bash Scripts?
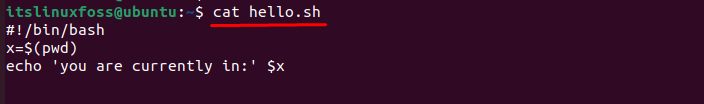
The “pwd” command is utilized in an existing “hello.sh” script file by storing the directory information in the “x” variable and displaying it through the “cat” command in the terminal as below:
$ cat hello.sh
Execute the script stored in the “hello.sh” file by navigating through the below command:
$ ./hello.sh
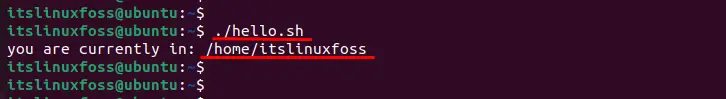
The output shows the current directory “/home/itslinuxfoss”, where the script file is placed.
How to Check the Previous Directory?
To find out the previous working directory, the “$OLDPWD” command utility is used with “echo” as below:
$ echo "$OLDPWD"
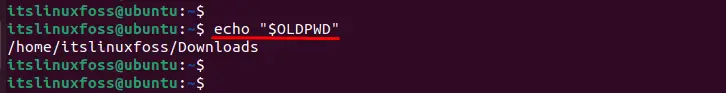
The output returns path “/home/itslinuxfoss/Downloads” on which previous work through this terminal.
How to Check the Version of pwd Utility?
To check the current version of the “pwd” command, first, get the path of the “pwd” utility as follows:
$ which pwd
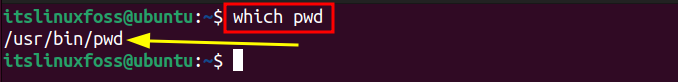
Or the path can also be retrieved via the command:
$ type -a pwd
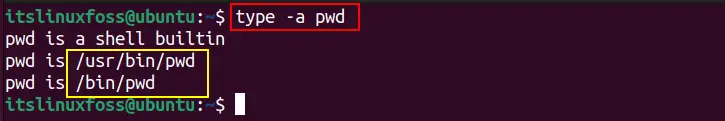
Now, use one of the paths with the “— version” option to get the installed version of the “pwd” utility:
$ /bin/pwd -version
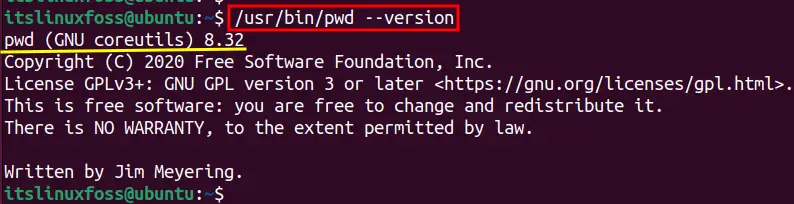
The execution returns the currently installed version of pwd as “pwd (GNU coreutils) 8.32”.
That’s all from this guide!
Conclusion
In Linux, the “pwd” command prints out the directory on which you are currently working. It rescues the system users when lost in multiple directories and provides an exact path from the root to the current directory. This guide has explained the pwd command with syntax and practical usage in the Linux operating system.
