Debian Backports are software packages that do not come with the stable release of Debian. They are available in the testing release or the upcoming release of Debian. Debian users can access the Debian Backports to download the recent releases of the packages which are not included in the installed stable Debian release.
Debian Backports allows users to access the new versions of the software and also ensures the stability of Debian stable. In this guide, the method of using the Debian Backports has been demonstrated with the step-by-step guide.
How to Use Debian Backports on Debian?
To download the packages from the Debian testing version to the Debian stable, follow all the steps mentioned below.
Step 1: Launch the Terminal
To execute the commands, open the terminal with the shortcut key CTRL+ALT+T:
Step 2: Access the Configuration File of Debian
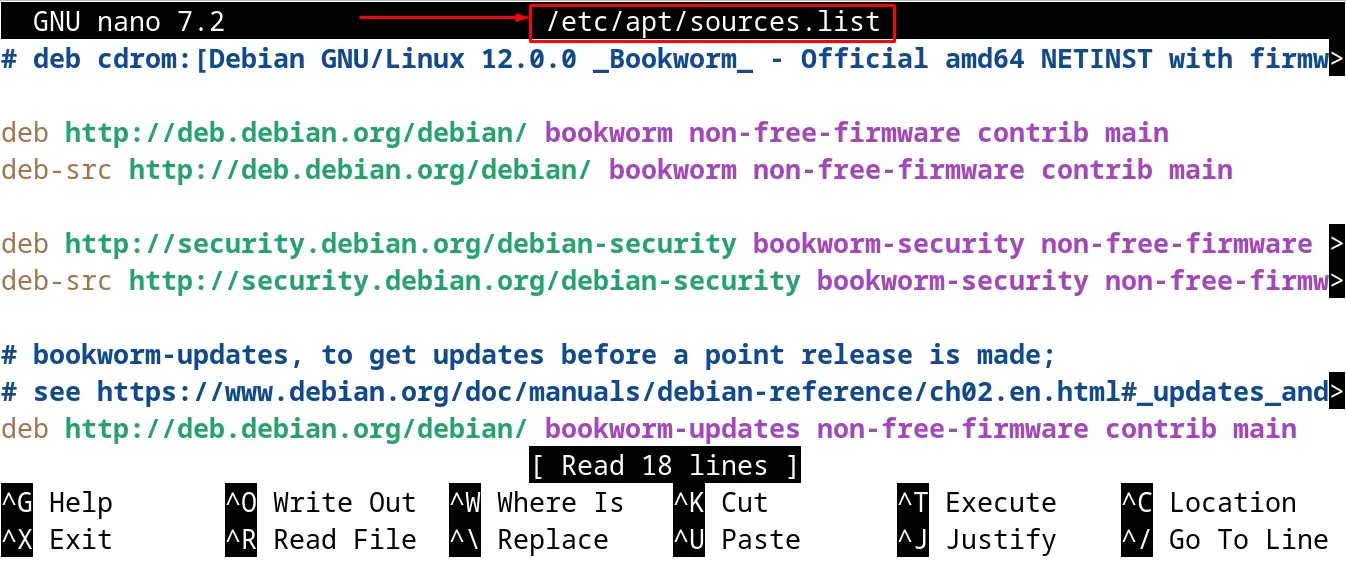
To access the configuration file of the Debian, use the nano text editor and run the command:
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Step 3: Edit the Configuration File
Edit the configuration file of the Debian by adding the following line at the end of the file:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm-backports main
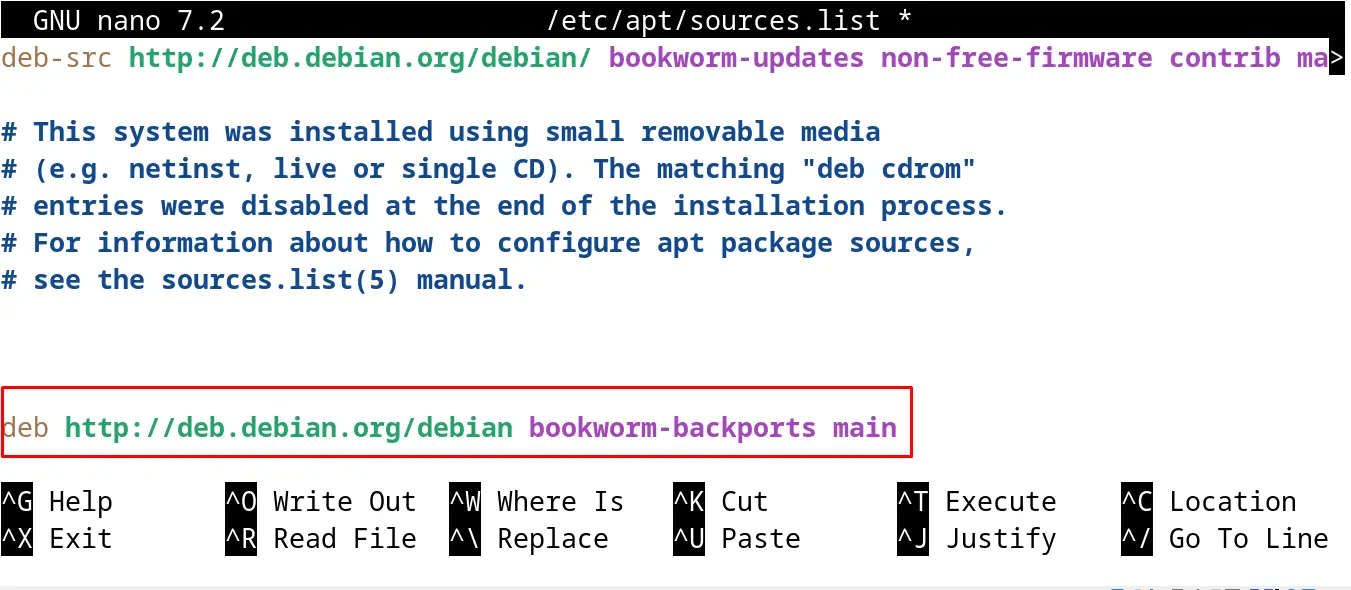
Note: In the above command, replace the “bookworm” with the name of the installed release for example, if Debian 11 is installed, then use the “bullseye”.
Save the file by pressing the keyboard shortcut of CTRL+S and terminate the text editor.
Step 4: Update the Debian
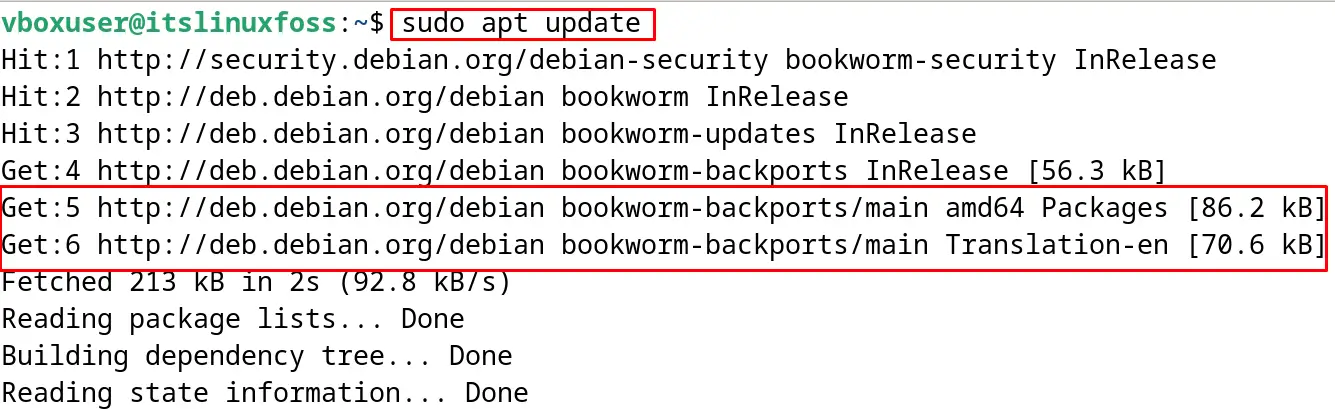
Now run the update option of the apt command to make sure all the packages are up to date:
$ sudo apt update
Step 5: Edit the Pic Configuration
To set the priority of the Debian Backports packages, open the configuration file of the backports:
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/preferences.d/backports.pref
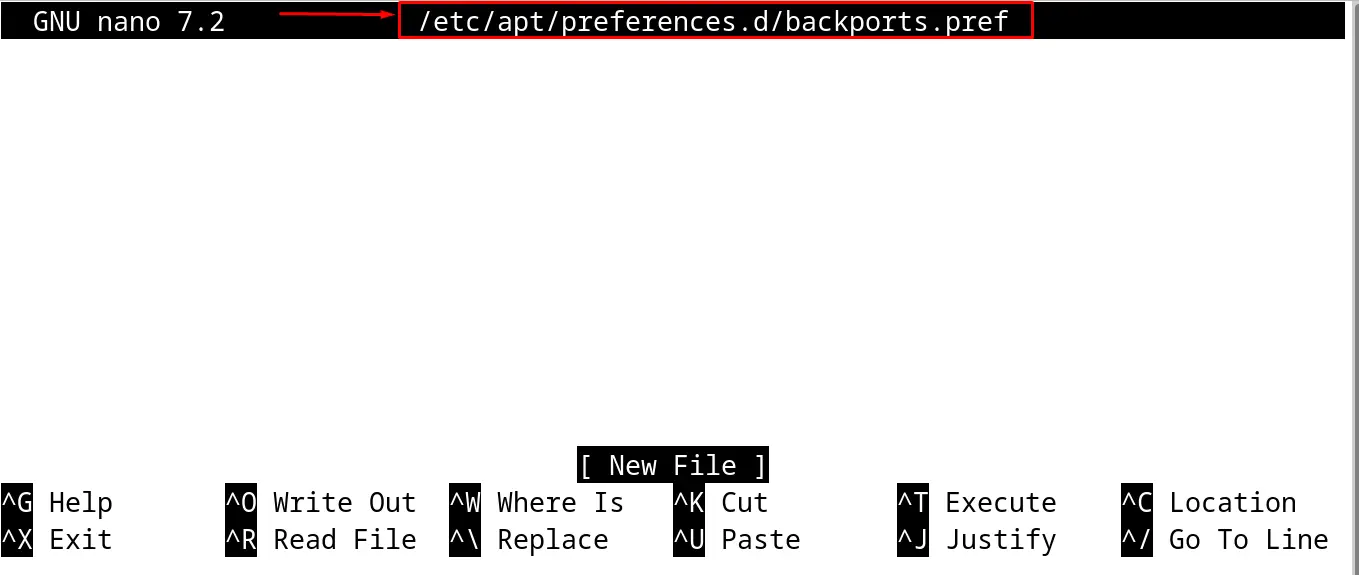
Add the below-mentioned lines in the configuration file:
Package: *
Pin: release n=bookworm-backports
Pin-Priority: 100

Exit the text editor after saving the file and proceed to the next step for the installation of the Debian Backports packages.
Step 6: Install the Debian Backport Package
To install the Debian Backport package on Debian, use the below-mentioned general syntax:
$ sudo apt install -t <codename>-backports example-package
To understand this, we will install the package of the “git-annex” available in the “bookworm-backports” using the command:
$ sudo apt install git-annex -t bookworm-backports
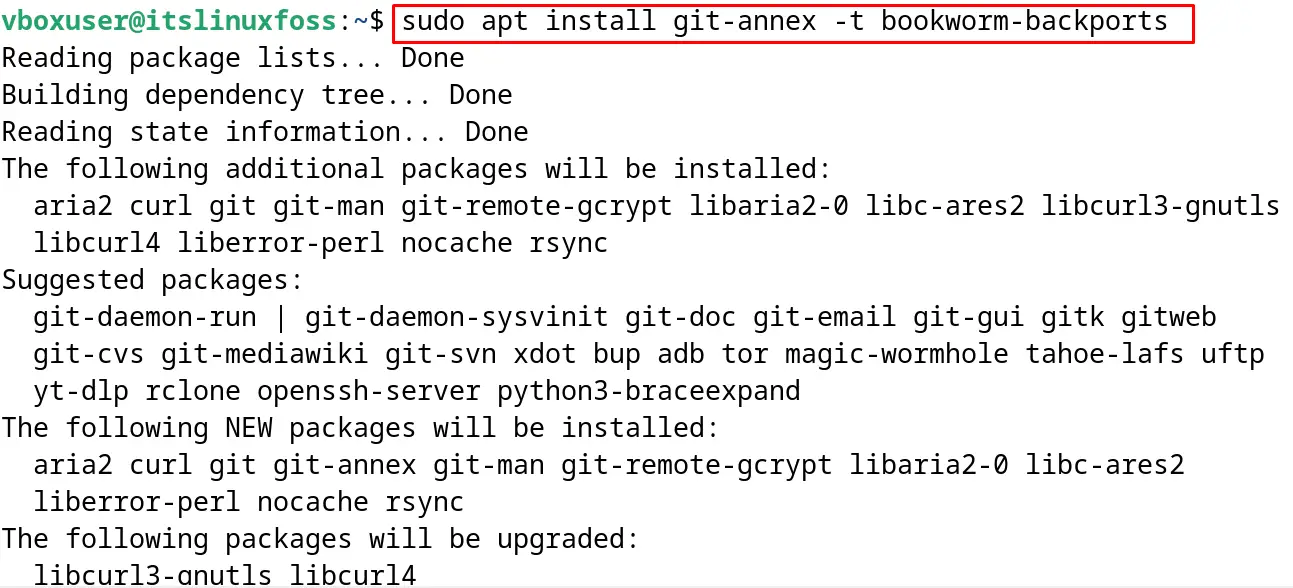
The Debian Backports package has been successfully installed on Debian.
How to Remove the Debian Backports Package from Debian?
To remove the Debian Backports package from the Debian, use the “remove” option of the apt command. For example, to remove the installed “git-annex” backport package from the Debian, run the command:
$ sudo apt remove git-annex -t bookworm-backports
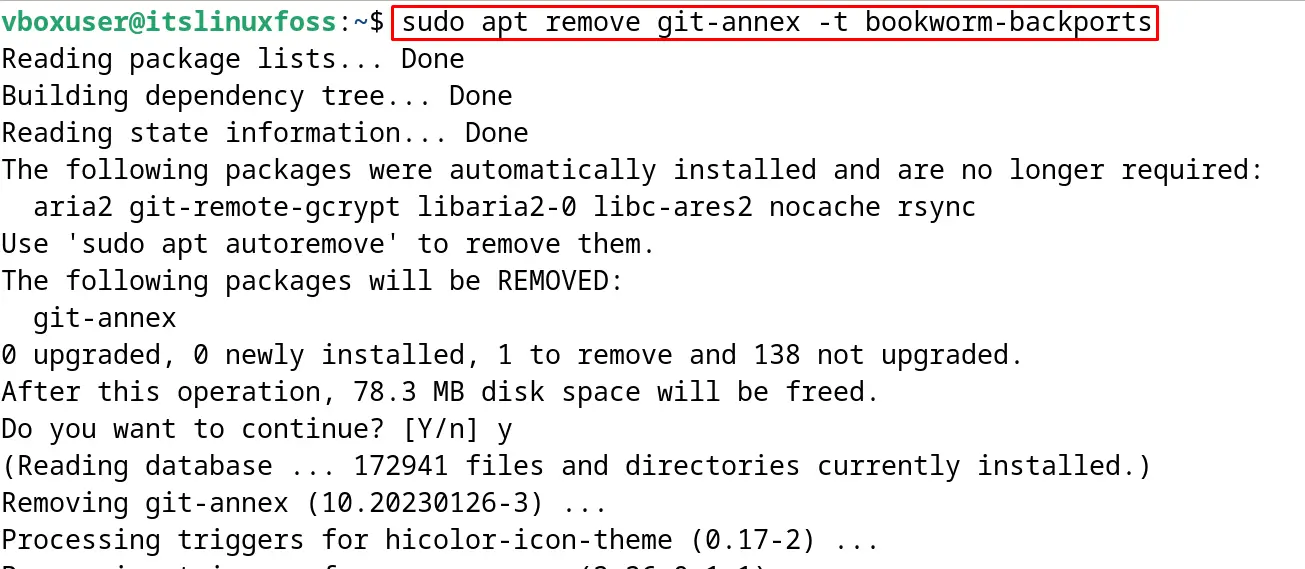
How to Remove the Debian Backports Repository from Debian?
To remove the entire repository of the Debian Backports, open the configuration file of Debian and remove the added line:
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
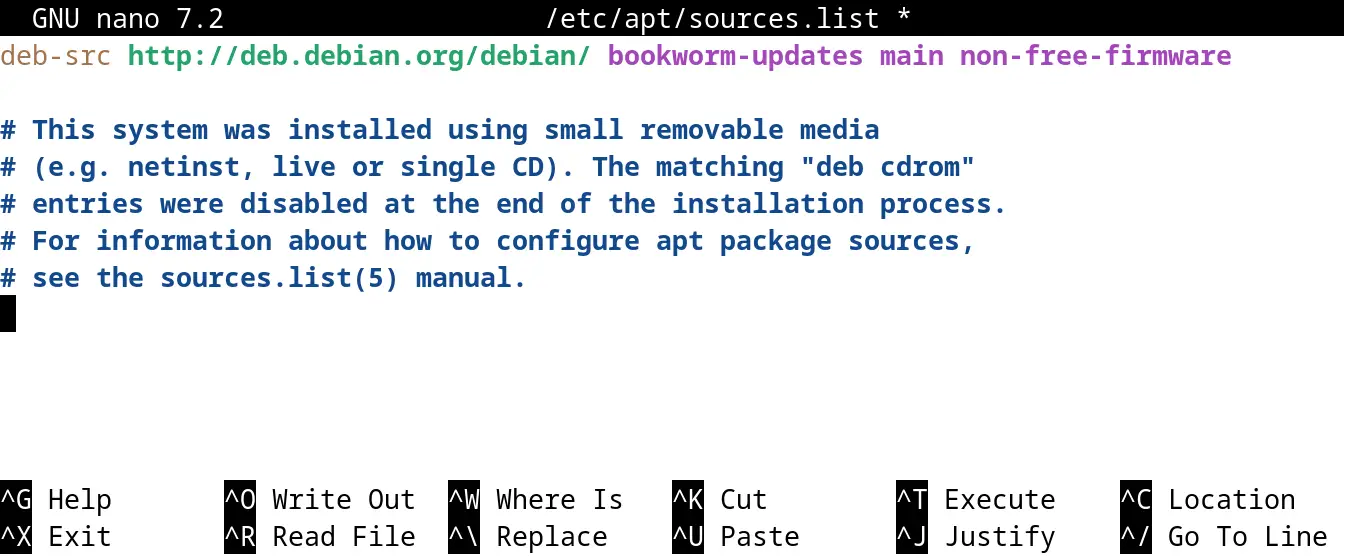
The repository of the Debian Backports has successfully been removed and to ensure it, run the update option of the apt command:
$ sudo apt update
This is the method of adding and using the Debian Backports repository on Debian.
Conclusion
To use the Debian Backport, open the configuration file of Debian and add the Debian Backports repository. This is added to use the software packages from the testing release. This post has explained the methods of adding and removing the Debian Backports repository. Also, discuss the commands to install and remove the Debian Backports packages on Debian.
