To mount and unmount drives on Debian 12 means to connect and disconnect the external storage drives on Debian 12 respectively. To share the data or to increase the storage memory of the computer, external storage drives are mounted to the Debian 12.
Similarly, when the storage drive is supposed to disconnect from the computer, it is recommended to first unmount the drive from the computer and this will prevent the data from being lost on the storage drive.
This blog will explain the methods to mount and unmount drives on Debian using the command-line interface.
How to Mount Drives on Debian 12?
To mount or connect the storage drives on Debian 12, follow the below-mentioned steps.
Step 1: Open the Terminal and Connect the Drive
First, connect the drive to the computer and launch the Debian’s terminal to run the commands:
Step 2: Find the Drive
To find out the name of the connected drive, run the command:
$ lsblk
It will display all the connected drives of the computer, and identify the new drive either from its name or size.
Step 3: Create a Mount Directory
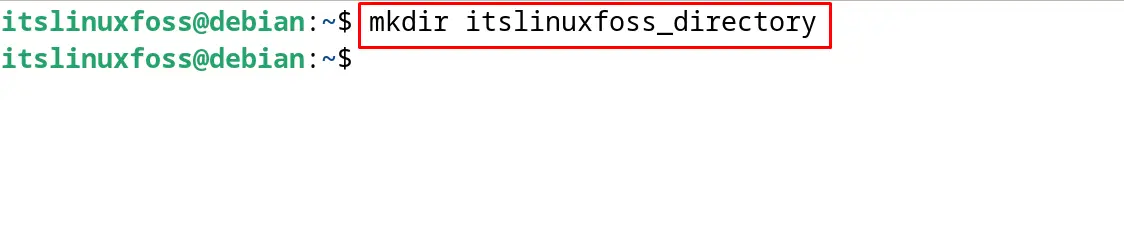
It is recommended to create a separate directory from where the drive’s contents can be accessed. This mount drive can be created using the mkdir command by specifying the name as shown:
$ mkdir itslinuxfoss_directory
Step 4: Mount the Drive
To mount the drive on the newly created directory, use the sudo privileges with the mkdir command:
$ sudo mount [device name] //mnt/itslinuxfoss_directory
Step 5: Verify the Mount
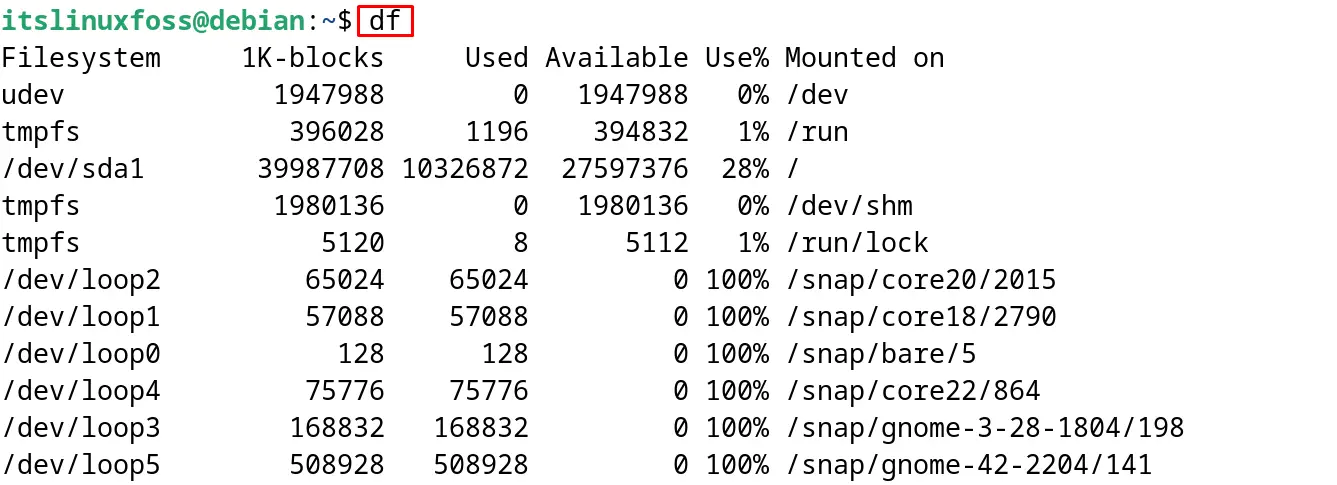
Use the “df” command to display the storage drives with their mount directories:
$ df

Step 6: Access the Drive
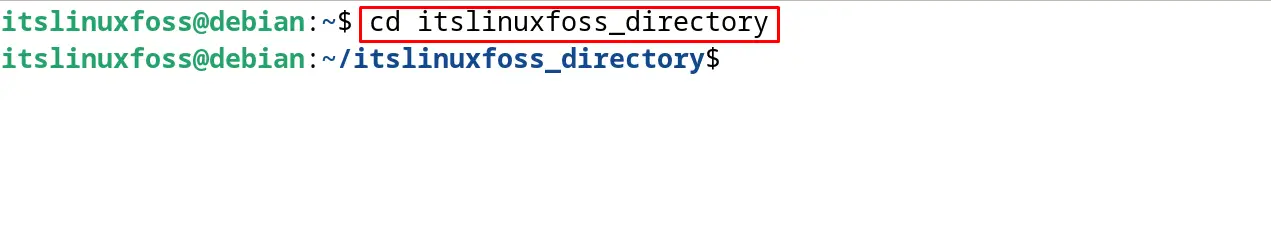
To access the drive, simply navigate to the newly created directory with the cd command:
$ cd itslinuxfoss_directory
Users can mount their drives on Debian 12 by following these simple six steps.
How to Unmount Drives on Debian 12?
To unmount or disconnect the drive from the Debian 12, use the “umount” command and specify the mount point of the drive:
$ sudo umount /mnt/itslinuxfoss_directory
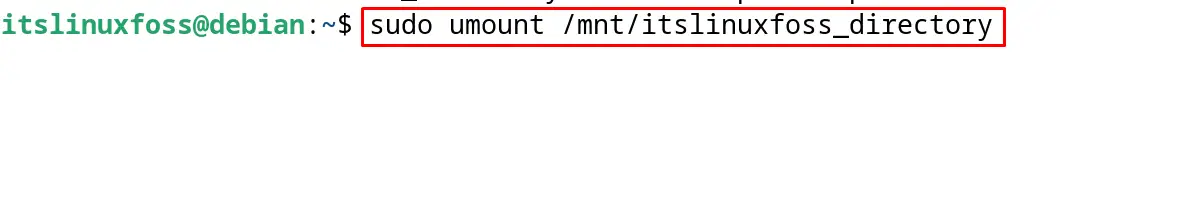
The device has been unmounted from the Debian 12 successfully.
This is all about mounting and unmounting the drives on Debian 12 using the command-line interface.
Conclusion
To mount the drive on Debian 12, connect the drive to the computer and create a directory to mount it. Run the “sudo mount [device name] [mount directory]” command in the terminal. The drive is mounted successfully on the computer. To unmount and remove it from Debian 12, run the “sudo umount [mount directory]” command. All the steps involved in the mounting and unmounting drives on Debian 12 have been explained in this blog.
