Python supports different modules and packages to do various programming tasks. The module named “math” is used in Python to perform various calculations on data using multiple functions. Some of the functions of the math module are factorial(), floor(), ceil(), exp(), log10(x) etc.
In this article, one of the functions of the “math” module named “math.ceil()” is demonstrated in depth using various examples. The following topics are part of our Python Guide:
- What is Python “math.ceil()” Function?
- Example 1: Ceiling of a Number Using math.ceil()
- Example 2: Errors in math.ceil() function
So let’s get started!
What is Python “math.ceil()” Function?
The “math.ceil()” function takes numeric data type values like int and floats and rounds up the given number to the nearest integer. The syntax of the “math.ceil()” function is shown below:
math.ceil(numeric expression)
The numeric expression value is required in the “math.ceil()” function to return its ceiling value in an integer.
Note: Boolean value (True and False) can also be passed inside the “math.ceil()” function. They will be utilized as “1 and 0”.
Let’s understand the working of this function with numerous examples given below:
Example 1: Ceiling of a Number Using math.ceil()
In the code given below, the “math.ceil()” function is used to find the ceiling number of different positive and negative float numbers
Code:
import math
print(math.ceil(222.7))
print(math.ceil(992.882))
print(math.ceil(-93.7))
print(math.ceil(-4.8))
print(math.ceil(49))
In the following code:
- The “math” module is imported in the program using the prefix “import”.
- The “math.ceil()” function is used with “5” different values in the above code, i.e., two “Positive float”, two ”Negative float” and one “Absolute integer” value.
- The positive value will round up to the nearest integer, and the negative float value will round toward zero.
Output:
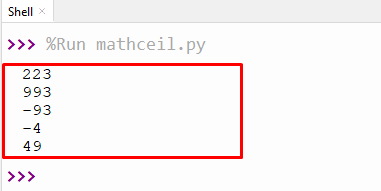
The output shows the ceiling value of numeric data.
Example 2: Errors in math.ceil() Function
When the positive or negative infinite value is passed in “math.ceil()” function. The function returns an “overflow” error as an output. Let’s understand via the following code:
Code:
import math
number = math.inf
print(math.ceil(number))
In the following code, the “math.ceil()” function throws an error when the infinite number is passed to it. The “math.inf” expression retrieves a floating point infinity.
Output:
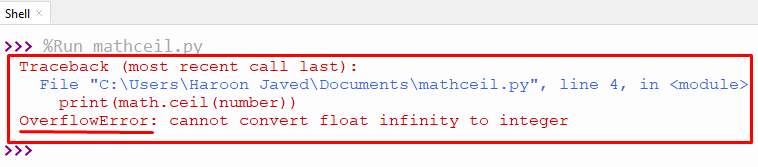
The output shows the “overflow error” of math.ceil() function.
That’s all from this guide!
Conclusion
In Python, the “math.ceil()” function takes positive or negative numeric values as arguments and rounds off the given numbers to the nearest integer. The “math.ceil()” function does not change the absolute integer value. This function gives an error when an infinite or undefined value is passed to it. This article provided all the details regarding the “Python math.ceil()” function with numerous examples.
