The essential network diagnostic tool is the traceroute command in Debian and other Linux distributions. It is used to track the routes of packets that are sent for sending some information across the IP networks.
The traceroute command is useful especially when the internet connection is having some issue or it is having trouble connecting to some IP address. In both cases, the route of the packets sent to that IP address can be found using the traceroute command. It will confirm whether the packets are sent in the right direction to access IP addresses or not.
This blog will explain the usage of the traceroute command on Debian 12 following the next-mentioned outline:
- How to Install the traceroute Command on Debian
- What is the Usage of the traceroute on Debian 12
- How to Uninstall the traceroute Command on Debian
Let’s start the post by installing the traceroute command utility on Debian.
How to Install the traceroute Command on Debian?
To install the traceroute command on Debian, open the terminal and update the package list with the following command:
$ sudo apt update
When the updation of the packages is completed, then install the “traceroute” command’s package with the execution of the command:
$ sudo apt install traceroute -y
Finally, display the version of the installed traceroute command as shown below:
$ traceroute --version

A displayed version of the traceroute command on Debian 12 is the confirmation of its successful installation.
What is the Usage of the traceroute on Debian 12?
To diagnose the network issues for establishing the connections with the IP network, use the traceroute command following its general syntax as shown:
$ traceroute [options] host_Address
To understand the usage of the traceroute command on Debian, different examples are used in the next section.
Example 1: Find the Track of Sent Packets with the traceroute Command
The traceroute command can be run to find out the track of the packets sent to the specific IP address by running it without any options. For example, to find the track of the itslinuxfoss IP address, run the command:
$ traceroute itslinuxfoss.com
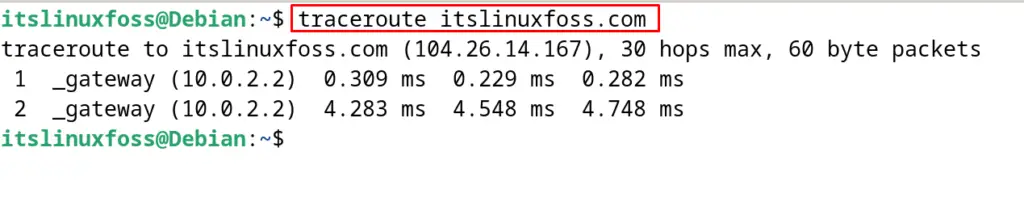
This output will display the information on the IP address and round-trip times as well.
Example 2: Find the Track by Specifying the Packets with the traceroute Command
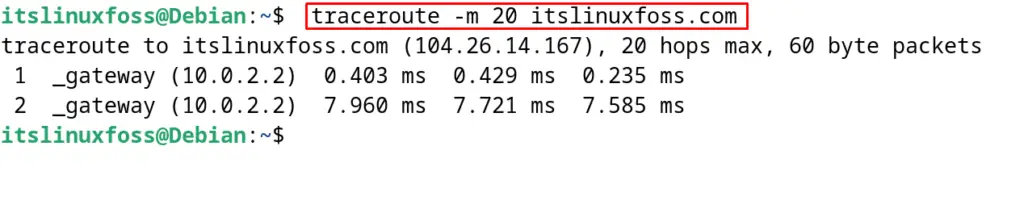
One can also specify the number of hops or the time to live of the packets, after which the packets are not supposed to be sent. For example, set the hops to 20 with the traceroute command:
$ traceroute -m 20 itslinuxfoss.com
Example 3: Find the Track by Specifying the Wait Time of Reply
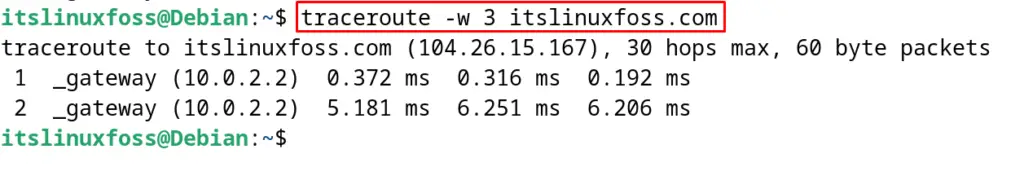
Also, the traceroute command can be executed by specifying the wait time of the reply from the IP address. For example, we want the traceroute command should try to establish the connection for 3 seconds, then use the command:
$ traceroute -w 3 itslinuxfoss.com
Example 4: Displaying the IP Address Using the traceroute Command
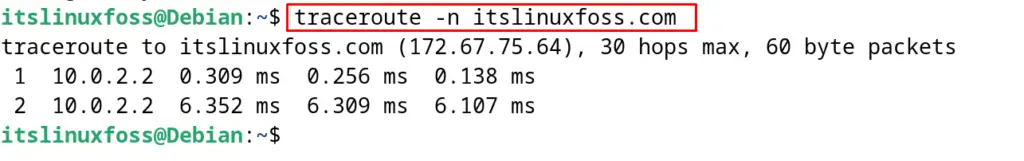
To display the IP address of a specific hostname, use the “n” option of the traceroute command as shown:
$ traceroute -n itslinuxfoss.com
Example 5: Trace the Route of Packets Over IPv6
To trace the connection by routing it over the IPv6, use the traceroute6 command as shown below:
$ traceroute6 itslinuxfoss.com

This command should work only if the specified IP address supports the IPv6.
Example 6: Trace the Route of Packets Using the UDP
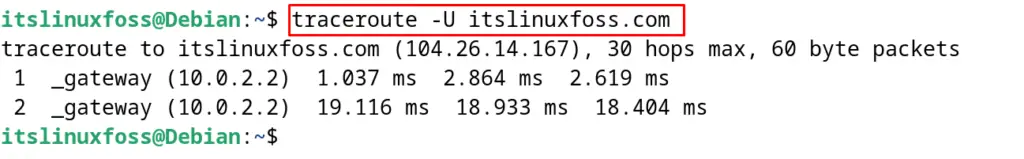
To use the UDP packets instead of the ICMP, use the “U” option of the traceroute command:
$ traceroute -U itslinuxfoss.com
Example 7: Trace the route of Packets by Specifying the Different Ports for UDP Packets
To use the UDP packets along with the ICMP packets, users can use the “p” option to assign a new port for UDP packets:
$ traceroute -p 1005 -U itslinuxfoss.com

In the above command, the “p” option is used to specify the port, and the “U” option is used to send the UDP packets.
Example 8: Change the Default Gateway Using the traceroute Command
To use some other gateway instead of the default gateway, run the command:
$ traceroute -g 192.168.10.1 itslinuxfoss.com

Example 9: Use the Specific Interface with the traceroute Command
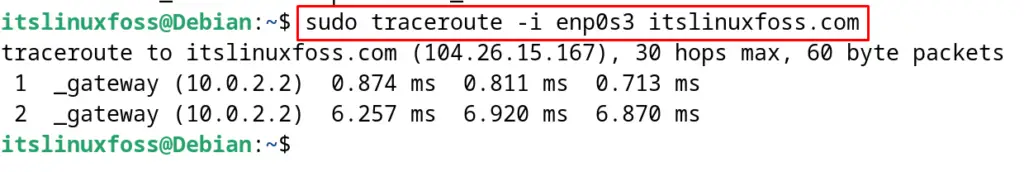
To use the specific interface among the multiple available interfaces, use the “i” option of the traceroute command:
$ sudo traceroute -i enp0s3 itslinuxfoss.com
To display more options for the traceroute command’s usage, open its manual by running the command:
$ man traceroute
How to Uninstall the traceroute Command on Debian?
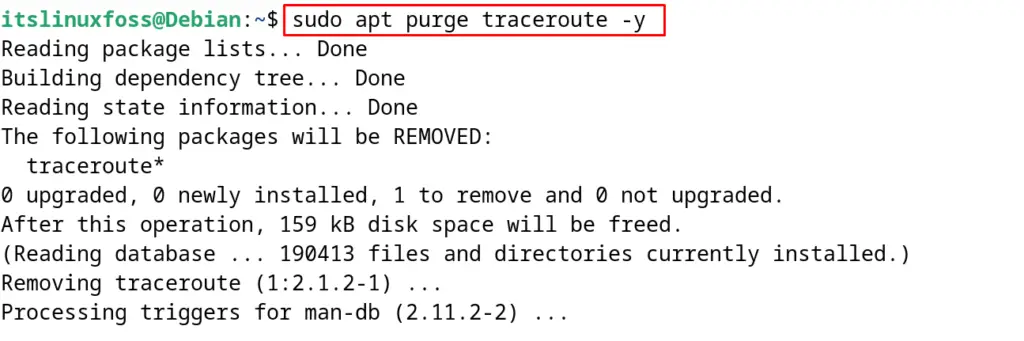
To uninstall and remove the traceroute command package on Debian 12 including its configuration files, run the command:
$ sudo apt purge traceroute -y
This is all about the usage of the traceroute command on Debian.
Conclusion
To use the traceroute command, open the terminal and follow the “traceroute [options] host_Address ” general usage syntax of the command.
The traceroute command is used to track the routes of the packets sent across the IP networks. This post has explained the installation of the traceroute command and its usage by demonstrating different examples.
