Debian is one of the most known Linux distributions that has the following of millions of people across the world. It comes with hundreds of Debian packages of different software and utilities. These Debian packages contain the configuration files, dependencies, and library files that are required for the installation of specific software.
Debian packages are installed and managed in Debian either by using the terminal or a graphical user interface. This blog will explain the removal methods of installed debian packages on Debian 12 and also answer the following outline:
- What is Debian Package Management?
- What are the Methods of Removing the Debian Packages in Debian 12?
- Method 1: Remove a Debian Package Using the apt Package Manager
- Method 2: Remove a Debian Package Using the dpkg Package Manager
- Method 3: Remove a Debian Package Using the GUI Interface
- How to Remove the Unused Dependencies in Debian 12?
- How to Clear Cache Package Files in Debian 12?
Let’s start the post by understanding Debian Package Management.
What is Debian Package Management?
The Debian and Debian-based Linux distributions come with a number of packages of different software that can be installed on them. These packages either be included in the official repository of the Debian-based Linux distributions or can be downloaded with the extension of the “deb”.
To manage these packages on Debian-based distributions, a graphical user interface method, and different command-line package managers can be used. The important command-line package managers are the “apt” and the “dpkg” package manager.
Both the mentioned package managers are used for the installation, upgradation, and removal of the Debian packages in Debian.
What are the Methods of Removing the Debian Packages in Debian 12?
Three different methods can be used for the removal of the Debian packages on Debian 12:
- Using the apt Package Manager
- Using the dpkg Package Manager
- Using the GUI Interface
All the mentioned above methods have been explained in detail for the removal of the Debian packages.
Method 1: Remove a Debian Package Using the apt Package Manager
The apt (Advanced Package Tool) is the package manager that comes by default in the Debian-based Linux distributions including Ubuntu. It contains different advanced options including the search, and shows how to manage the Debian packages.
The general syntax of using the apt command in Debian-based Linux distribution:
$ sudo apt [option] [package_name]
The options of the apt command which are used to remove the Debian packages on Debian 12 are:
| Options of apt Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
| remove | This option is used to remove the installed software |
| purge | This option is used to remove the installed software with their configuration files |
| autoremove | This option is used to delete the unused dependencies |
To understand the usage of the above-mentioned option of the apt command for the removal of Debian packages, three examples have been used.
Example 1: Usage of the remove Option of the apt Command
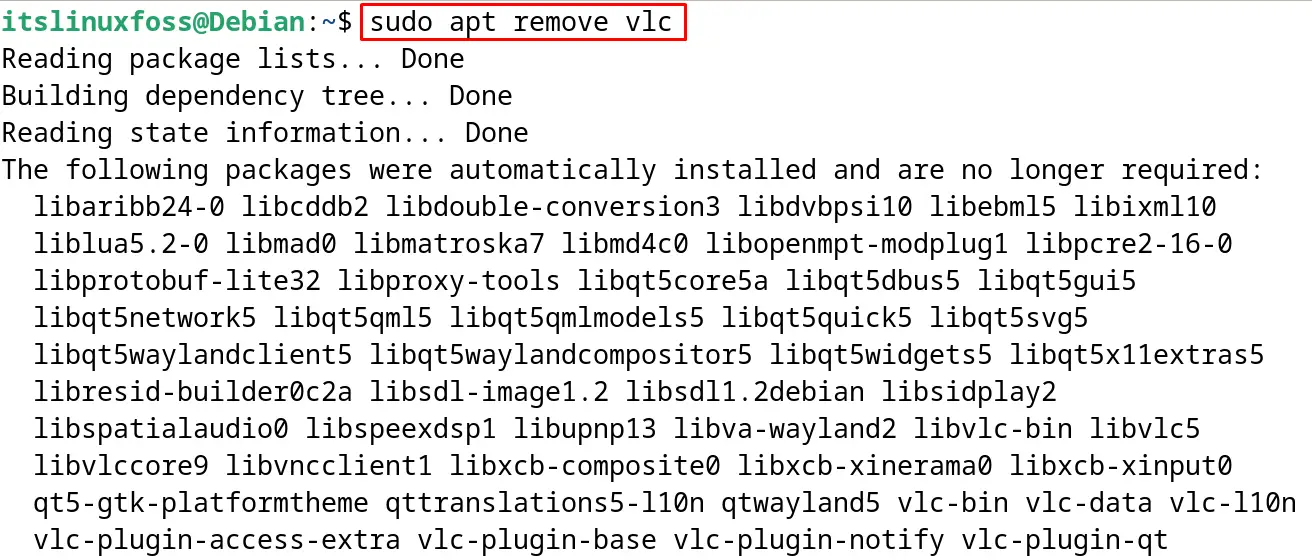
To remove the “VLC” package from the Debian, run the command:
$ sudo apt remove vlc
Example 2: Usage of the purge Option of the apt Command
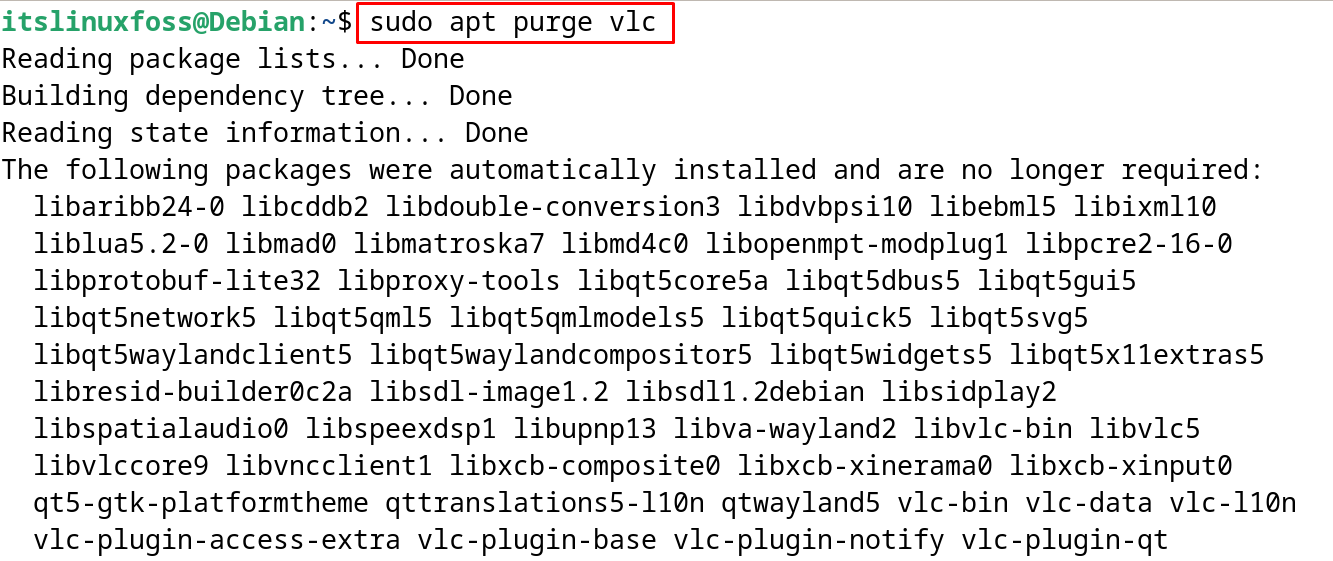
To remove the “VLC” with all its configuration files, use the “purge” option:
$ sudo apt purge vlc
Example 3: Usage of the autoremove Option of the apt Command
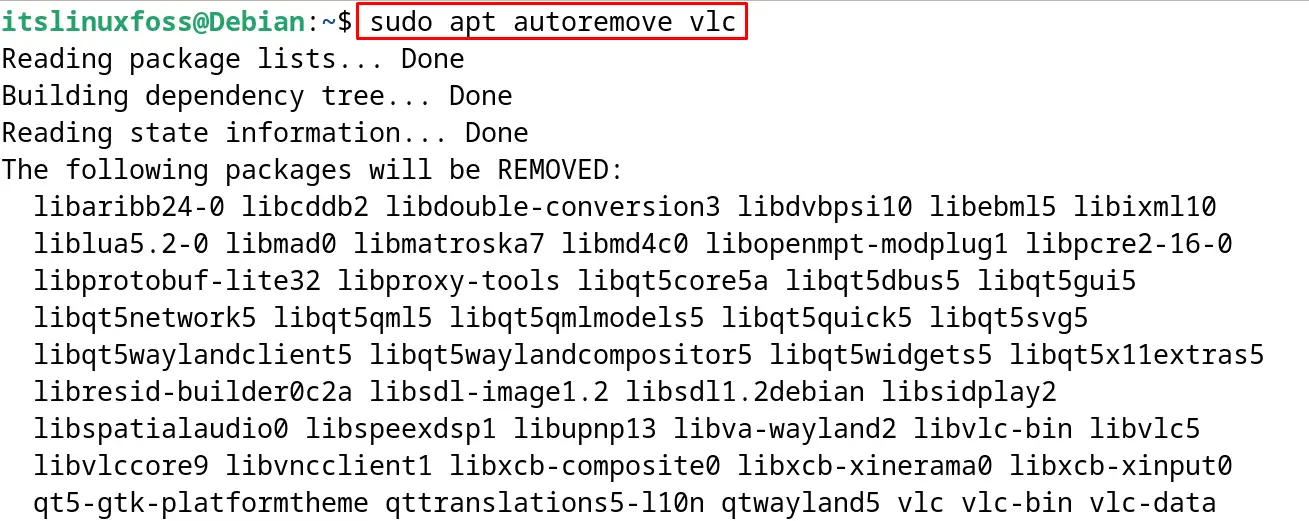
To remove the unused dependencies of the “vlc”, run the apt command with the “autoremove” option:
$ sudo apt autoremove vlc
These are the different options of the apt command that are used to remove the Debian packages.
Method 2: Remove a Debian Package Using the dpkg Package Manager
The dpkg is the primary package management tool in the Debian-based distributions. This package is especially useful for managing the packages with the “deb” extension.
The general syntax of using the dpkg command:
$ sudo dpkg --[option] [package name]
Two different options of the dpkg package manager are used for the removal of the Debian packages:
| Options of dpkg Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
| remove | Used to remove the installed packages excluding the configuration files |
| purge | Used to remove the installed packages including the configuration files |
Both options of dpkg for the removal of the packages are explained with examples.
Example 1: Usage of the remove Option of the dpkg Command
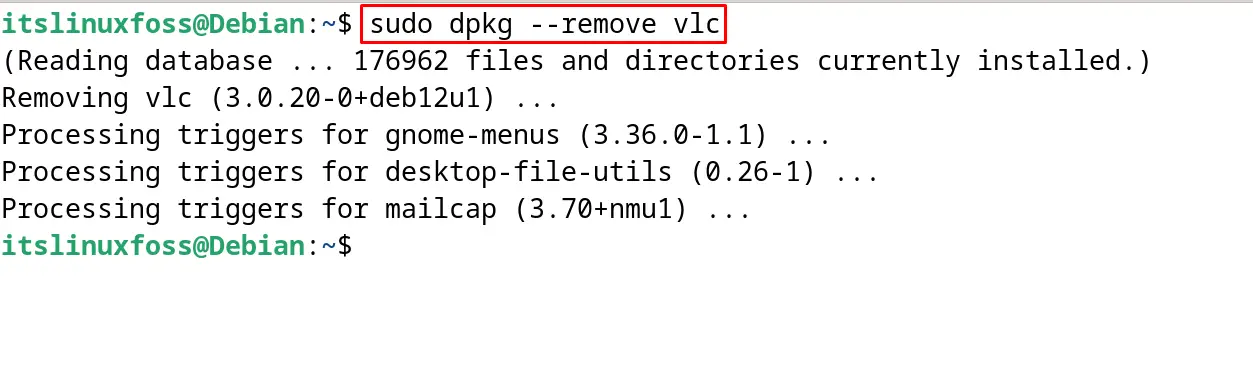
To remove the installed package without its configuration files, run the command:
$ sudo dpkg --remove vlc
Example 2: Usage of the purge Option of the dpkg Command
To remove the installed debian package with the configuration files, execute the command:
$ sudo dpkg --purge vlc
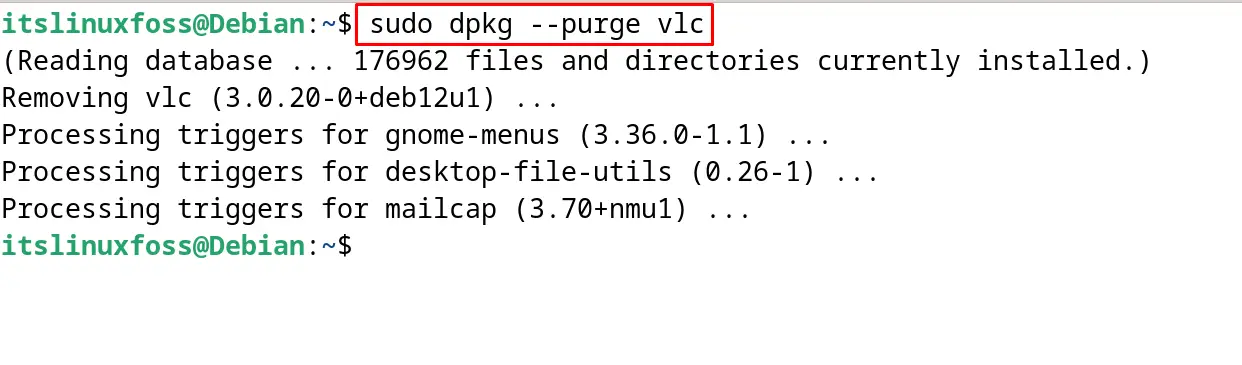
Example 3: Remove the Packages with the force Option
Use the “force flag” if the package is not being deleted due to a dependency issue:
$ sudo dpkg --remove --force-all vlc
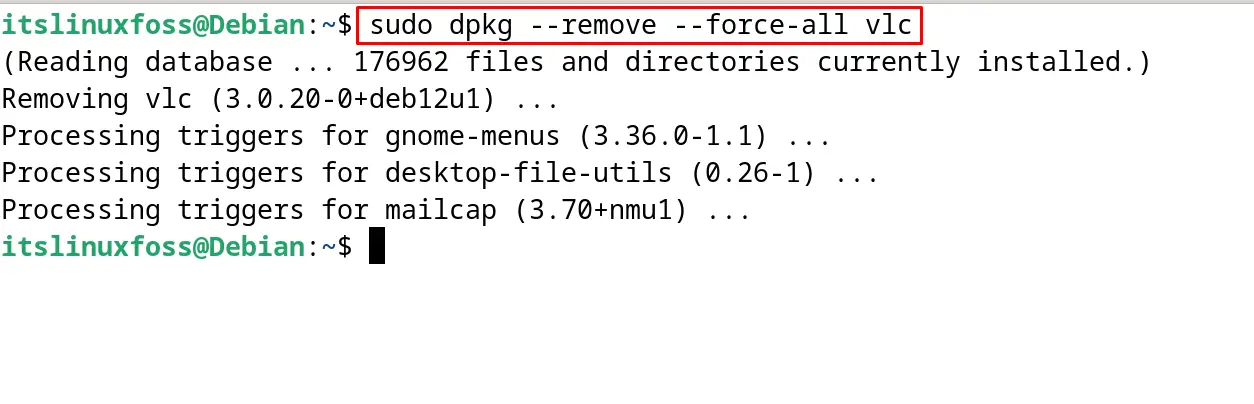
These options can be used to remove the Debian packages with the dpkg command.
Method 3: Remove a Debian Package Using the GUI Interface
The last method to remove the installed packages from the Debian 12 is by using the Graphical User Interface. For this, open the “Software” by searching from the application list:
Then click on “Installed” and a list of the installed applications will be displayed:
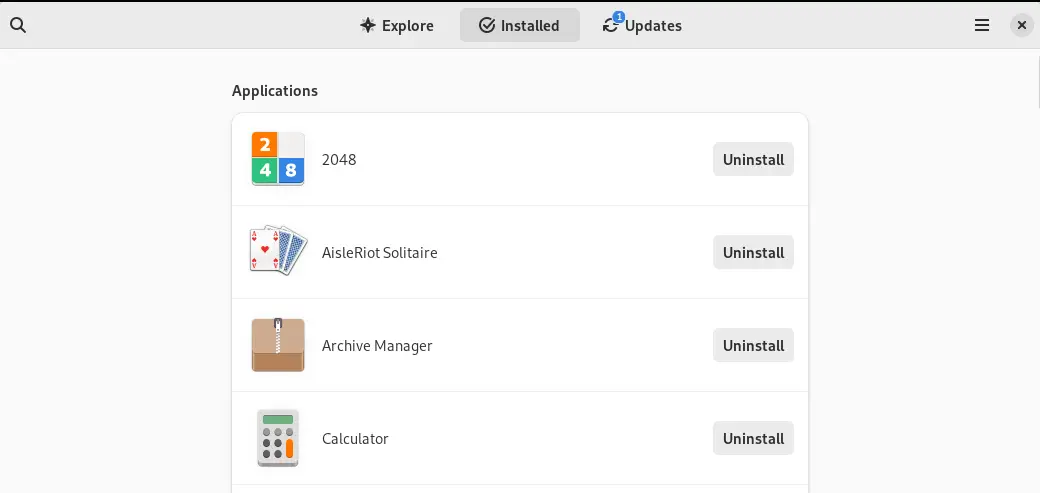
Find the application that is supposed to be uninstalled by scrolling down the screen. For example, in our case the “VLC” is supposed to be uninstalled:
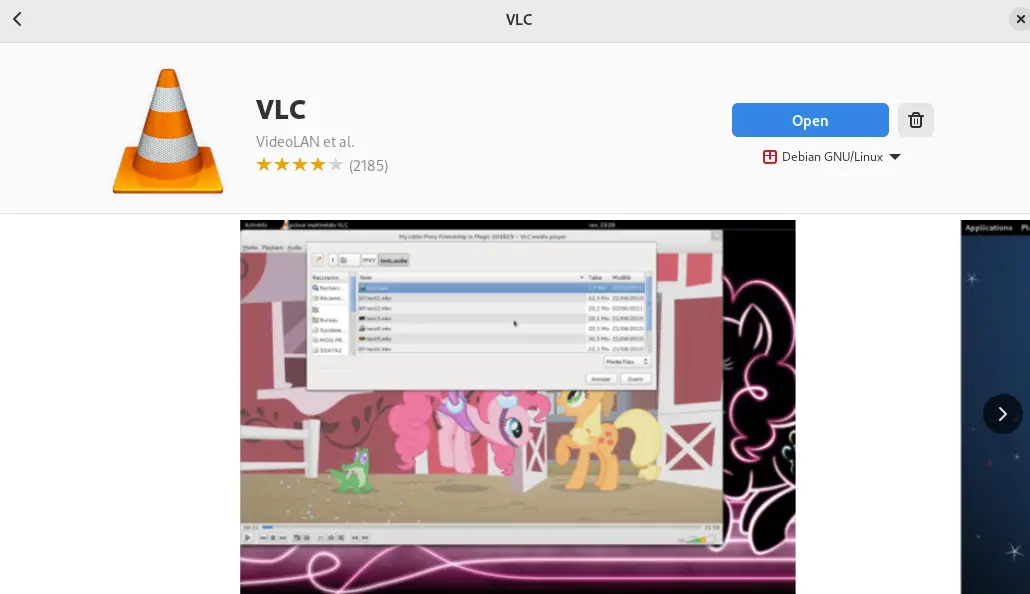
Now click on the “Delete” icon to uninstall and remove the application from Debian 12:
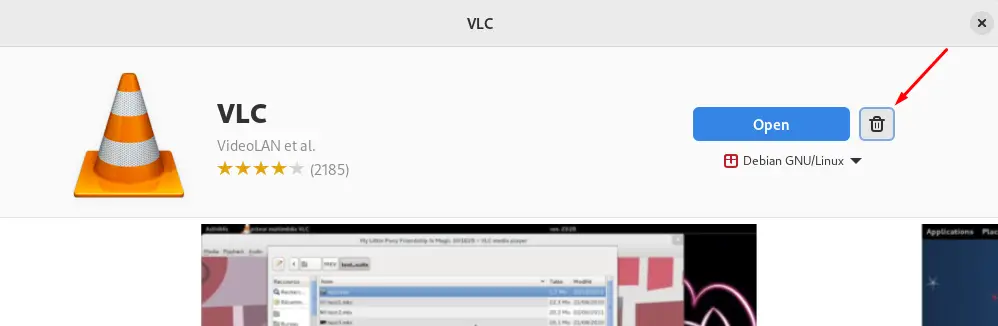
Click on the “Uninstall” button to proceed with the uninstallation:
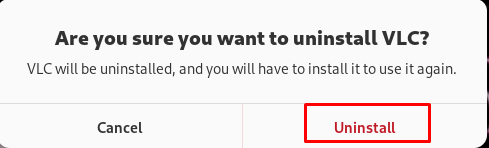
Finally, type the root password to confirm the uninstallation:
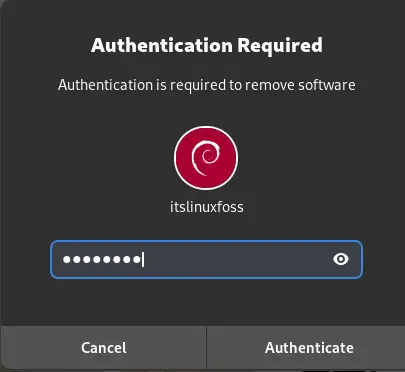
The application has successfully removed and uninstalled on the Debian 12:
How to Remove the Unused Dependencies in Debian 12?
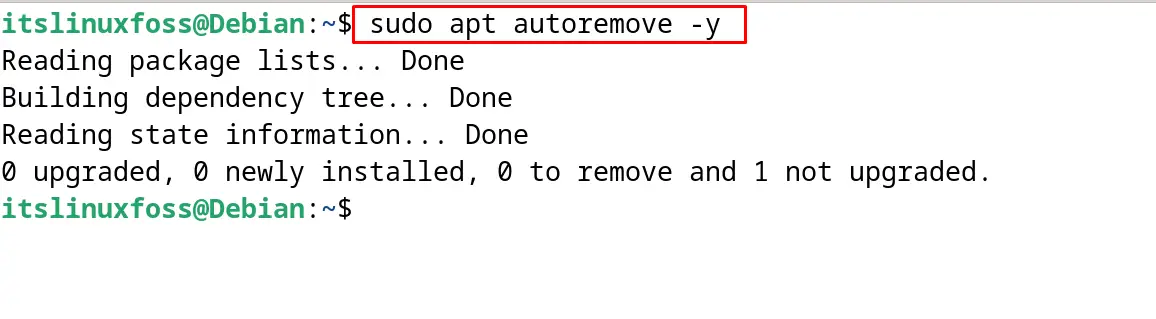
To remove the unused dependencies on Debian 12, use the “autoremove” option of the command. It will help to free up the space on the memory usage:
$ sudo apt autoremove -y
How to Clear Cache Package Files in Debian 12?
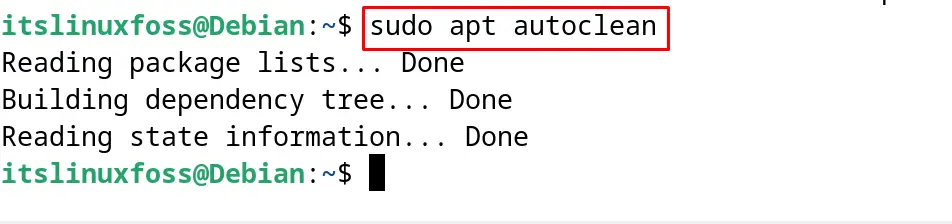
To clear the cache files of the installed debian packages, run the command:
$ sudo apt autoclean
All these methods and commands are used for the removal of the Debian packages on Debian 12.
Conclusion
To remove a debian package on Debian 12, the apt package manager, the dpkg manager, and the graphical user interface methods can be used. All these methods have been explained in detail with the examples in this post. The options of the apt command and dpkg command which are used for the removal of the debian package have also been explained. Moreover, this post also explained the commands to remove unused dependencies and cache files to free the memory space.
