The “PATH” environment variable is a variable that keeps a list of directories that the system explores for executable files. This allows users to run programs easily without defining the entire path to the .exe files. Additionally, users can set or update the “PATH” variable by assigning the new directory path.
This article will demonstrate various methods to show PATH environment variables in Linux.
- Using the “echo” Command
- Using the “cat” Command
- Using the “env” Command
- Using the “set” Command
- Using the “printenv” Command
Method 1: Using the “echo” Command
The “echo” is one of the most commands to show the “PATH” environment variables by executing with the symbol “$” in the Linux terminal:
$ echo $PATH
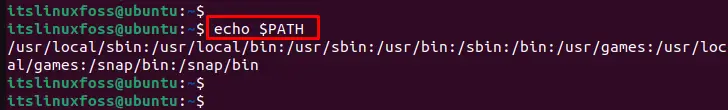
The output shows the complete path of environment variables in the terminal.
Method 2: Using the “cat” Command
To show the PATH of the environment variable, you can execute the “cat” command with the “/etc/environment” file. Additionally, the “grep” command is utilized to fetch the value of the PATH variable and display it in the terminal:
$ cat /etc/environment | grep PATH
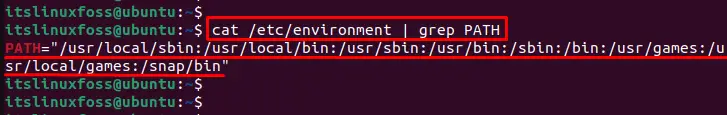
The command visualizes the path of an environment variable.
Optional: Update the PATH Environment Variable
To update the “PATH” variable, the “export” command is utilized to assign the new directory to the “PATH” variable. In our case, specify the path “home/itslinuxfoss” to the “PATH” as below:
$ export PATH=$PATH:/home/itslinuxfoss

In this way, a new path “/home/itslinuxfoss” is set to the “PATH” environment variable.
Method 3: Using the “env” Command
Users can utilize the “env” command that fetches the value of “PATH” environment variables via the “grep” command:
$ env | grep PATH
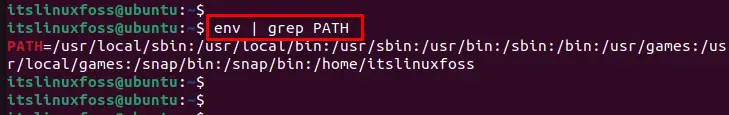
The output visualizes the complete path of an environment variable.
Method 4: Using the “set” Command
To view the PATH environment variable, you can execute the “set” command with the “grep” by specifying the “PATH” variable in Linux:
$ set | grep PATH
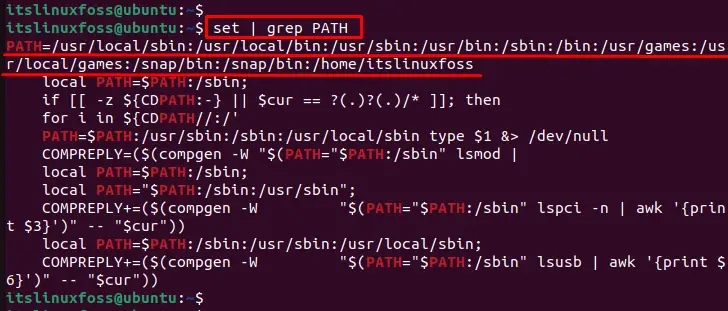
The outcome of the above command returns the “PATH” value of the environment variable.
Method 5: Using the “printenv” Command
You can view the value of the PATH variable by executing the “printenv” command:
$ printenv PATH
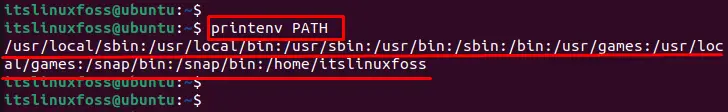
The above execution shows the path of environment variables in linux.
Conclusion
To show the PATH of an environment variable, execute the “echo“, “cat“, “env“, “set“, and “printenv” commands with the “PATH” variable. It comprises the number of directories the system requires to execute configuration files. Additionally, users can set or update the “PATH” variable by assigning the new directory path via the “export” command. This article has explained all possible methods to show the PATH of an environment variable in Linux.
