Time is an important thing to live in this world as all our duties and tasks are related to time. Every zone of the continent follows its time zone which is different from the others. For example, if users are living in Europe they might experience the daytime and meanwhile, users living in Asia will experience evening or nighttime.
When users are moved to some other country, it is recommended to synchronize the gadgets and computers according to that country. Now there are two possibilities, either the users set the time manually according to the country or synchronize it with the internet. With the change of the location of the IP address, the computer device will automatically set its time.
This blog will explain the methods to synchronize the time on Debian following the outline:
- What is the Network Time Protocol (NTP) on Debian
- How to Install the Network Time Protocol on Debian
- How to Set Up the Time Sync on Debian
- How to Switch from the ntpd to timesyncd on Debian
What is the Network Time Protocol (NTP) on Debian?
The network time protocol (NTP) is the protocol that ensures the computer should have the actual time by synchronizing the time with its network time servers. When no network is available on the Debian machine, then systemd-timesyncd behaves as the NTP.
How to Install the Network Time Protocol on Debian?
The Network time protocol comes pre-installed on Debian but if it is not installed, then run the following command:
$ sudo apt install ntp -y
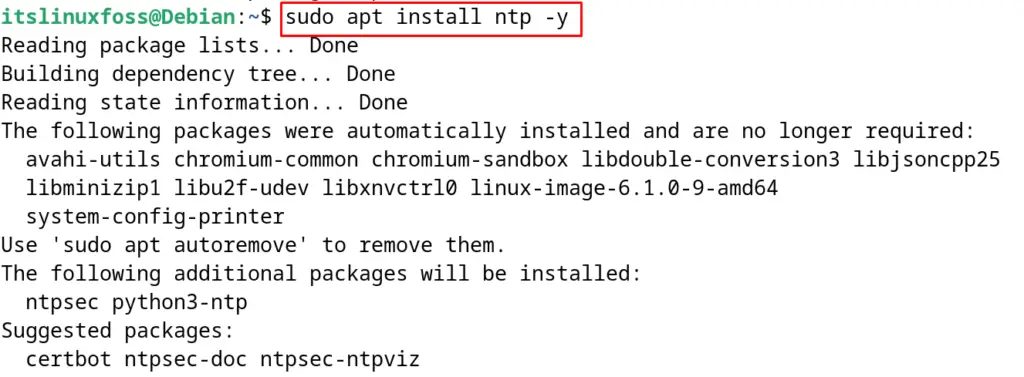
This is the installation package of the network time protocol daemon. To display the status of the NTPd, use the command:
$ sudo systemctl status ntp
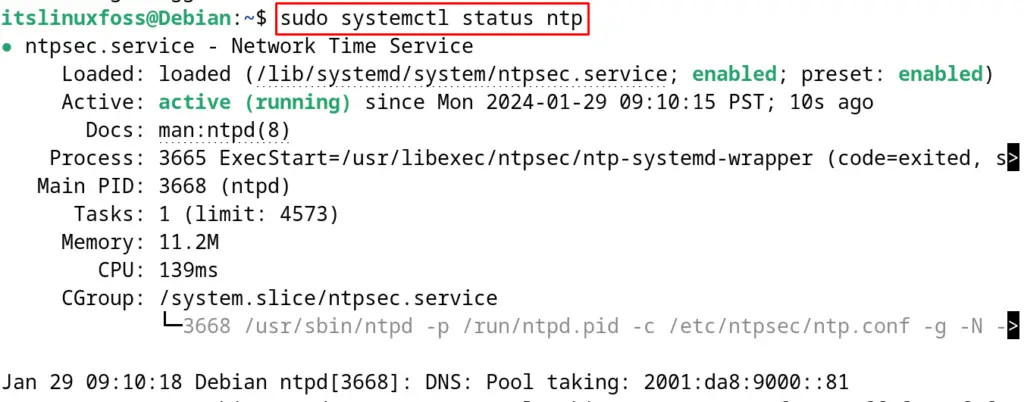
How to Set Up the Time Sync on Debian?
To set up the time sync on Debian, follow the instructions explained in the next steps.
Step 1: Launch the Terminal
To set up the time sync on Debian, launch the terminal from the application’s menu:

Step 2: Display the Date
To display the current date on Debian, run the command:
$ date

Step 3: List the Timezone
Now list down all the available time zones by running the command:
$ timedatectl list-timezones
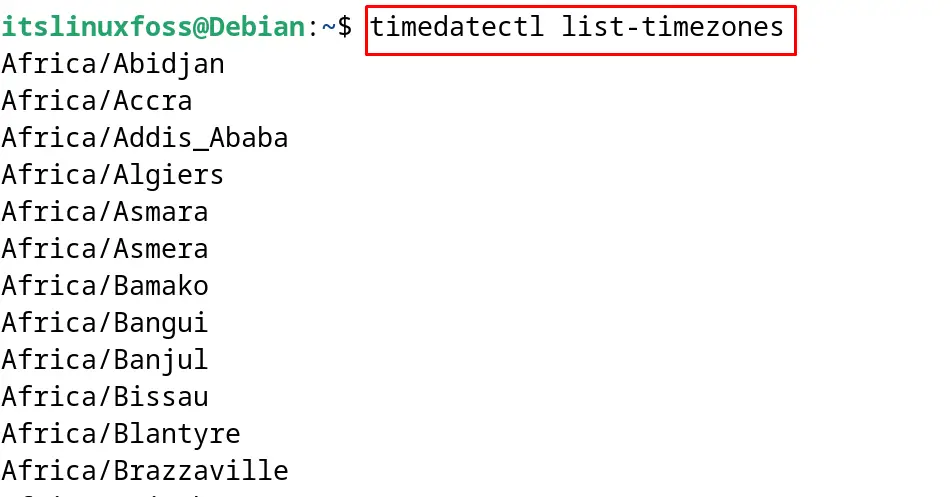
In the output, different time zones can be seen such as African continent with its countries. Note the time zone that is supposed to be set and press the q key to exit from the menu.
Step 4: Set the Timezone
Now use the noted time zone and run the command mentioned below to sync time with it:
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone US/Eastern

In our case, we use the US/Eastern time zone for the demonstration purpose.
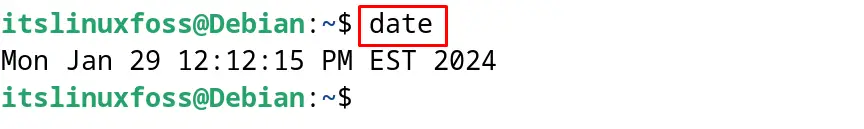
Step 5: Display the Time
To confirm the changes, again display the time with the following command:
$ date
How to Switch from the ntpd to timesyncd on Debian?
The timesyncd package is the alternative to the ntp on Debian and other Linux distributions. To use the timesyncd package on Debian, it is necessary to delete the ntp package by running the command:
$ sudo apt purge ntp -y
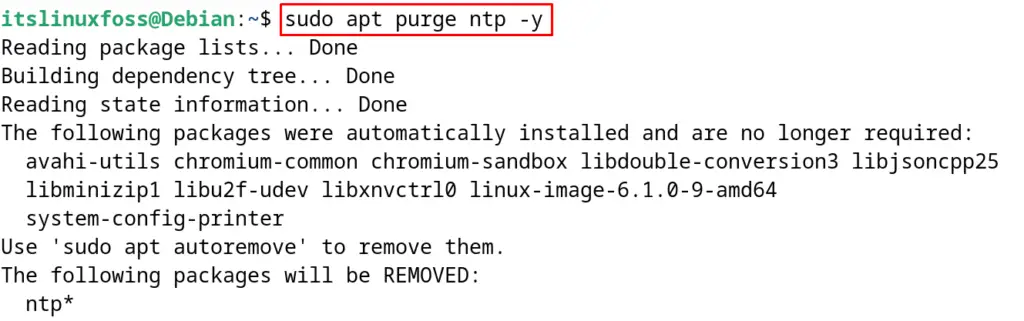
When the package of network time protocol daemon is uninstalled successfully, then install the timesyncd by running the command:
$ sudo apt install systemd-timesyncd -y
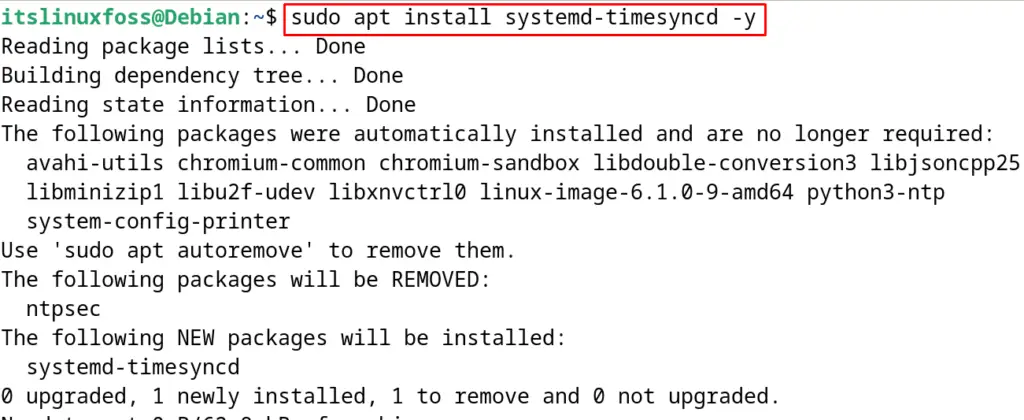
After the installation is completed, start the service of the timesyncd with the next mentioned command:
$ sudo systemctl start systemd-timesyncd

Check the status of the timesyncd service:
$ sudo systemctl status systemd-timesyncd
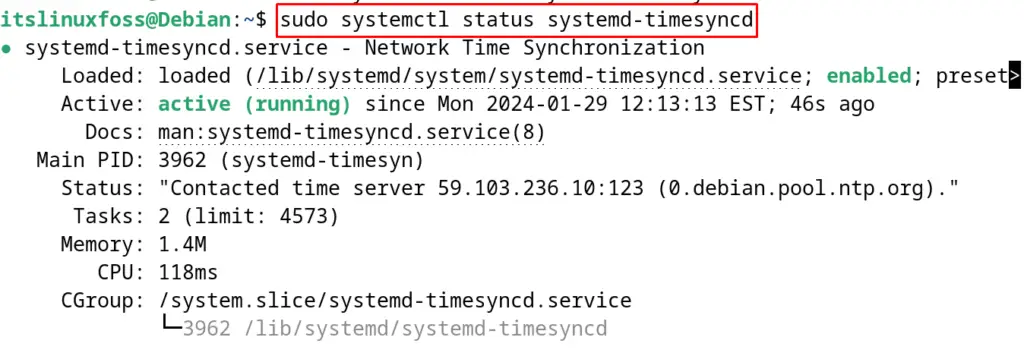
Finally, display the time with the following command:
$ timedatectl
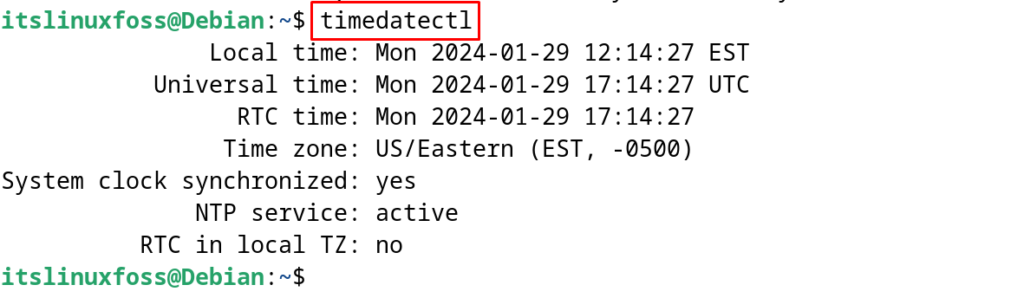
This is the way to sync the time using the timesyncd package on Debian.
Conclusion
To sync the time on Debian 12, either use the network time protocol or the timesyncd package on the terminal. Make sure that only one package from the mentioned is installed at a time.
These packages will help the users to synchronize the time with the current time of the location. This blog has explained both packages to install the sync time on Debian with the step-by-step guide.
