Linux displays the file or directory permissions held by the user via the “ls -l” command. These permissions are of three types: “read”, “write”, and “execute”. The “read” permissions are represented by “r”, and “write” permissions are identified by “w”, and the “execute” is denoted by “x” in Linux.
The “cannot create directory permission denied” error in Linux is a common problem that occurs when a user tries to create a new directory in a location where they do not have the required permissions. This error prevents the user from creating the directory and may cause frustration or confusion.
This guide describes the causes and possible solutions for the issue “cannot create directory permission denied”. The outline of this article is as follows:
- What is the “cannot create directory permission denied” Error in Linux?
- What are the Reasons for the “cannot create directory permission denied” Error in Linux?
- How to Fix the “cannot create directory permission denied” Error in Linux?
- Reason: Permissions Not Granted
- Solution 1: Allow the Directory Permissions
- Solution 2: Change the Directory Ownership
- Solution 3: Create the Directory with Root Privileges
- Solution 4: Create the Directory in a Different Location
- Solution 5: Check the Disk Space and Quota Limits
What is the “cannot create directory permission denied” Error in Linux?
This error in Linux is a common problem that occurs when the user tries to create a new directory in a location where they do not have the required permissions.
There are several possible reasons why this error may occur, such as incorrect ownership, group membership, access mode of the parent directory, or insufficient disk space or quota limits. The solution to this error depends on the specific cause and the user’s privileges.
What are the Reasons for the “cannot create directory permission denied” Error in Linux?
The “cannot create directory permission denied” error can happen for various reasons, such as incorrect ownership, group membership, or access mode of the parent directory. In some scenarios, the user is not the owner of the parent directory or does not belong to the group that owns it, the parent directory has restricted permissions that do not allow the user to create subdirectories.
Also, the user is trying to create a directory in a system or protected location that requires root or sudo privileges and the user has exceeded their disk quota or the disk is full.
How to Fix the “cannot create directory permission denied” Error in Linux?
To fix this “cannot create directory permission denied” error, use the “sudo” command to run the command as a superuser or change the ownership or permissions of the target directory via the “chown” or “chmod” commands. Also, users can create a new directory in a different location where they have written access.
Let us get into the reasons and the solutions with the practical implementation:
Reason: Permissions Not Granted
The error “cannot create directory permission denied” occurs because the currently logged-in user does not have the “write” permissions to create the directory. Suppose the user runs the “mkdir” command to create the directory “test” in the “home” directory. It will not create as in the below error screenshot:
mkdir test
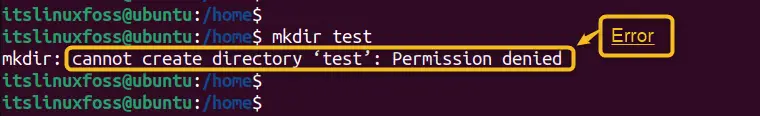
To resolve this type of error, the user needs to access the write permissions of the “test” directory. Let us fix this error via multiple solutions:
Solution 1: Allow the Directory Permissions
One possible way to fix the error “cannot create directory permission denied” in Linux is to allow directory permissions. This means changing the access rights of the directory where users want to create a new subdirectory. For this, use the command “chmod” to modify the permissions of a directory.
Let us follow the below steps for practical implementation:
Step 1: Create a Directory with Sudo Privileges
To create the directory, use the “mkdir” command with the directory name by specifying the “sudo” privilege. It allows users to create the directory with the read permission:
sudo mkdir test

In this way, the “test” directory has been created with sudo privileges.
Step 2: Check Directory Permissions
Now, check the “test” directory permissions with the “ald” flag to enlist directory contents of files and directory via the below-mentioned command:
ls -ald test
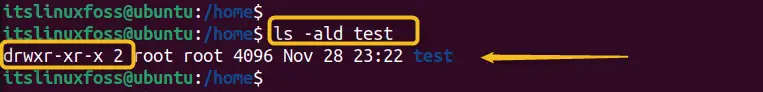
The owner does not have the “write” permissions to create the subdirectory as it only reads the “test” directory.
Note: For more details about the file/directory permission, follow our guide on “Linux Permissions”:
Step 3: Change Directory Permissions
Change the “test” directory permissions to create the subdirectory inside it. For this purpose, use the “chmod(Change Directory)” command with the combination of “a+w” and the target directory name in the terminal. The “a+w” flag allows the users “all” and “write” permission to “test” directory:
sudo chmod a+w test

In this way, the “test” directory has the “write” permissions.
Step 4: Verify Directory Permission to Create Subdirectory
Execute the “ls” command again to verify the new changes along with the “ald” flag to enlist directory contents of files and directory with permissions:
ls -ald test
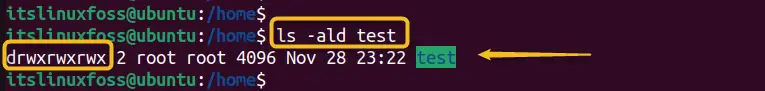
The output confirms that now the “test” directory has the “write” permissions to create a directory inside it.
Now run the “mkdir” command by specifying the subdirectory named “subtest1” in the terminal. Now the below command will create the “subtest1” directory without any error:
mkdir test/subtest1

The output verifies that the error “cannot create directory permission denied” has been fixed now, and the “subtest1” is created successfully inside the “test” directory.
Alternative Way 1: Using Absolute Mode
To change the permissions of the directory/subdirectory, execute the “chmod” command with the 777 flag with the directory name. It allows anyone to write to it and gives read, write, and execute permissions to the owner, group, and others:
sudo chmod 777 test/subtest1

In this way, the “test” directory has the read, write, and execute file permissions to all users.
Alternative Way 2: Using Symbolic Mode
A better option is to use the “chmod” command by specifying the permission to the directory as “u+rwx,g+rwx,o+rx directory_name”. It gives full permissions to the owner and the group, and only read and execute permissions to others as below:
sudo chmod u+rwx,g+rwx,o+rx test
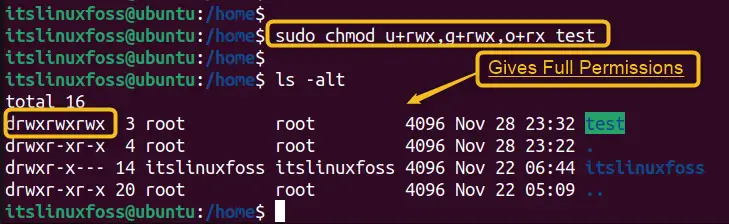
In this way, the above-mentioned permission has been granted.
Solution 2: Change the Directory Ownership
One solution to fix the “cannot create directory permission denied” error in Linux is to change the directory ownership. This means that you can assign a different user or group as the owner of the directory. After that, grant them permission to create files or subdirectories inside it.
To perform this task, change the ownership of the specified directory via the “chown” Linux command.
The syntax along with the explanation is given below:
Syntax
Run the below syntax in the terminal to make the current user an “owner” of the directory:
sudo chown -R "$USER:" /path/to/the/directory
The above syntax contains the following components:
- chown: Linux command that is useful to change the ownership of file/directory.
- R: This flag represents “recursive” as it changes the ownership of files and subdirectories located in a directory.
- $USER: The current user replaces the global variable.
- path/to/directory: Shows the specified directory path.
Here are the steps to change the directory ownership:
Step 1: Check the Current Owner and Group of the Directory
Use the “ls -l” command to check the current owner and group of the directory:
ls -l
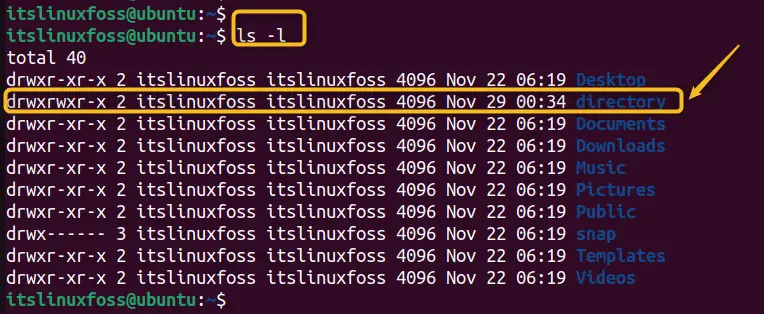
The first column shows the permissions, the third column shows the owner (root), and the fourth column shows the group (root).
Step 2: Change the Owner and/or Group of the Directory
Use the “chown” command to change the directory’s owner and/or group. You can specify a new owner, a new group, or both, separated by a colon.
For example, to change the owner to “roger” and the group to “itslinuxfoss”, utilize the below command:
sudo chown roger:itslinuxfoss directory
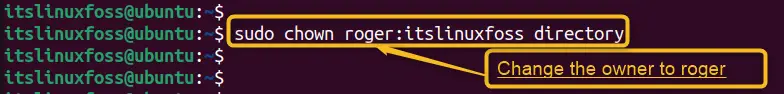
Users need to use “sudo” if they are not the current owner or root.
Step 3: Verify Ownership
Use the “ls -l” command again to verify that the ownership has changed.
ls -l
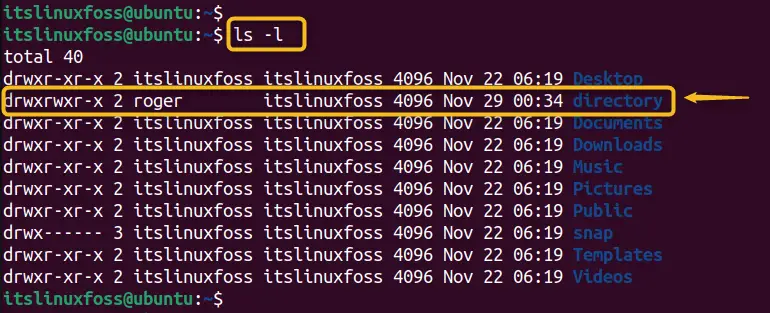
Now users can try to create a file or a subdirectory inside the “directory” as “roger” or as a member of the “itslinuxfoss” group. In this way, users will not see the permission denied error anymore.
Solution 3: Create the Directory with Root Privileges
One of the possible solutions to fix the error is to use the “sudo” command. It creates the directory with root privileges. It is possible if the user has sudo access and knows the root password.
Let us create a directory and subdirectory named “sampletest” and “test” in the root terminal:
sudo su # Switch Root
mkdir sampletest # Create Directory
mkdir sampletest/test # Create Subdirectory
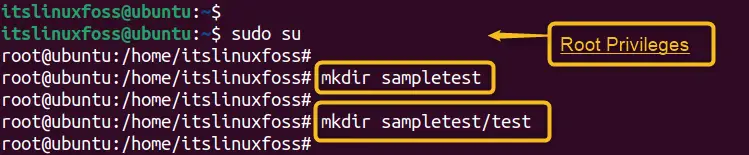
The above execution validates that the directory and subdirectory have been successfully created in the root terminal.
Solution 4: Create the Directory in a Different Location
One of the solutions is to create the directory in a different location where the user has to write permissions, such as their home directory or a temporary folder.
For instance, use the “mkdir” command by specifying the directory name as “directory1” in the “home” directory as below. Here, the “p” option creates the directory only if it does not exist:
mkdir -p /home/itslinuxfoss/Music/Rock
The output shows that the directory named “Rock” has been successfully created without an error.
Solution 5: Check the Disk Space and Quota Limits
Another solution is to check the disk space and quota limits using the “df” and “quota” commands, and free up some space or request more quota if needed:
df
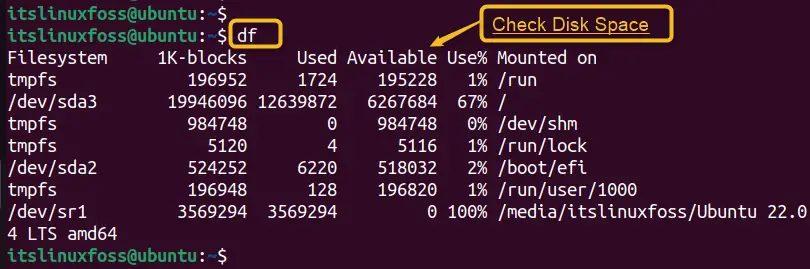
The output displays the disk space and whether the quota limit is exceeded or not. If the “Available” column has some space, users can create the directory in the specified file type, otherwise, remove some space from the system.
To explore more about free space from the Linux systems, check out our detailed guide on “Free up Disk Space in Linux”.
That is all about the reasons and the solutions to the error “cannot create directory permission denied”.
Conclusion
The “cannot create directory permission denied” can be resolved by allowing the directory permissions. The permissions of the desired directory can be changed by utilizing the “chmod (Change Directory)” command. Also, use the “sudo” command to run the command as a superuser or change the ownership or permissions of the target directory via the “chown” or “chmod” commands. Also, users can create a new directory in a different location where they have written access. This article has explained all the possible solutions to resolve the error “cannot create permission denied” in Linux.
