In Ubuntu, system administrators are able to access the system’s log files. These files are stored in the “/var/log” directory. They record various activities that take place on the system, such as system events, application logs, and user activities.
This guide will provide a method to access all major log file locations and visualize some of them in Ubuntu.
- Major Log Files Location in Ubuntu
- Access Log Directory
- View the System Log File
- View the Kernel Log File
- View the Authentication Log File
Major Log Files Location in Ubuntu
A log file is a record of system activity maintained by the operating system and various system services. It contains information about events, errors, warnings, and other important system activities, which can be useful for troubleshooting problems and monitoring system performance.
To access major log files in the “/var/log” directory, follow the below instructions:
Access Log Directory
To access the log files, open the terminal and navigate to the “/var/log” directory via the “cd” command.
It navigates to the log directory using the following command:
$ cd /var/log
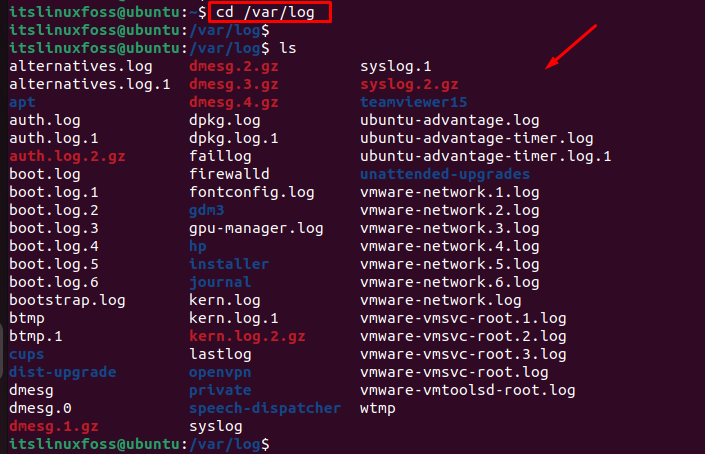
The above command displays all major log files including zip files, it is because log files grow over time and take up a lot of disk space. Therefore, zip files are created to store them.
View the System Log File
The “syslog” is the system’s main log file and it includes messages from all system daemons, such as the web server, database server, and more. To view this file, utilize the “less” command:
$ less syslog

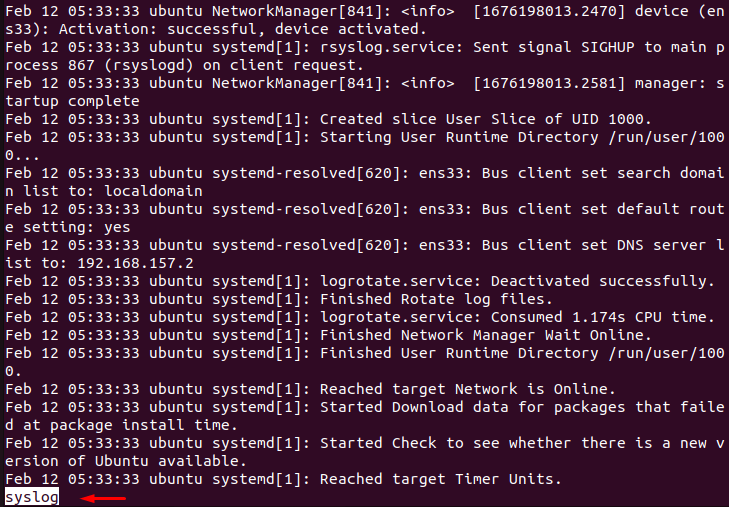
The output displays the contents of the “syslog” file containing the system logs.
View the Kernel Log File
The kernel log files are system log files that record information related to the Linux kernel. They provide low-level services to user programs and manage system resources such as memory, processors, and input/output devices.
To visualize the kernel log files, the “less” command is utilized by specifying the “kern.log” file:
$ less kern.log
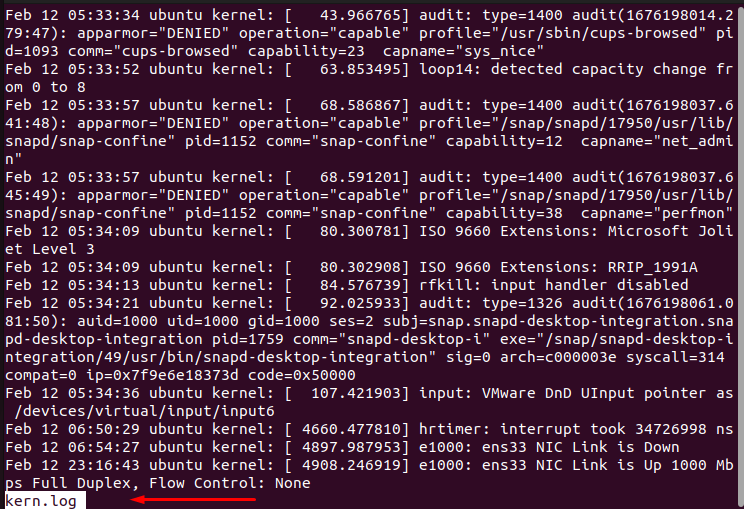
It displays the kernel logs in the terminal.
View the Authentication Log File
Using the “less” command, the content of the authentication log file can be displayed via the “auth.log” file:
$ less auth.log

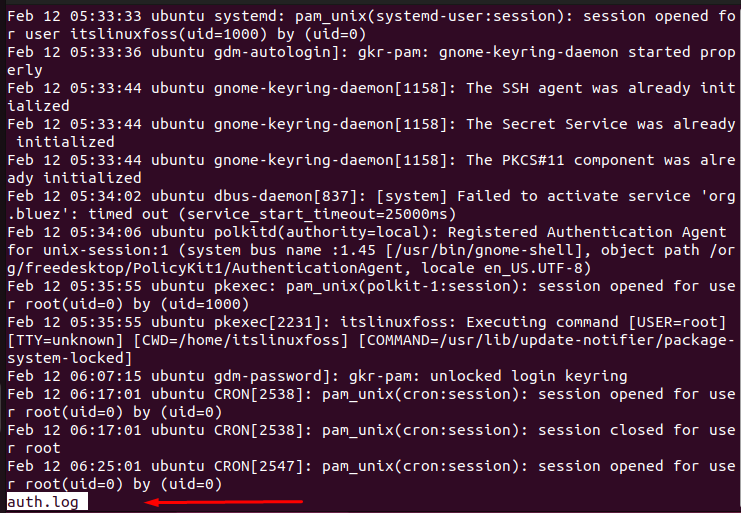
The execution of the above command visualizes the contents of the “auth.log” file having authentication logs.
Note: There are many other log files in the /var/log directory, and you can access them using the same method as described above.
Conclusion
In Ubuntu, all major log files are located in the “/var/log” directory. It includes “sys.log”, “auth.log”, and “kern.log” files which represent the system, authentication, and kernel log file, respectively.
This article has briefly explained the procedure to access the log files.
