YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) is a package management utility that is used in CentOS and RHEL. It manages the software installation, removal, and upgrading tasks based on the user as well as administrator requirements.
This article will demonstrate the YUM command with examples to install, remove and upgrade packages in CentOS.
How to Install a Package Using YUM?
To install a package using the YUM package manager, use the “install” utility by specifying the “package-name”. The syntax is provided below to install any package in CentOS:
Syntax:
$ sudo yum install package-name
The “package-name” refers to the package name that users want to install.
Example:
An example is considered to install the Apache server by mentioning the package name “httpd-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.5”:
$ sudo yum install httpd-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.5
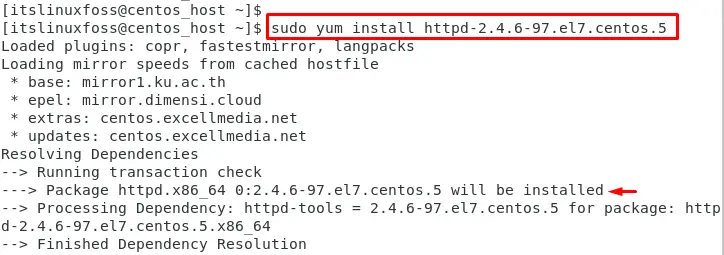
This command installs the Apache web server along with its dependencies.
How to Remove Packages Using YUM?
To remove a package using YUM, use the “remove” utility by mentioning the package name. The basic syntax to remove any package is mentioned below:
Syntax:
$ sudo yum remove package-name
In the above syntax, the “package-name” identifies the name of the package that users want to remove from CentOS.
Example 1: Remove Only Executables
The “httpd-2.4.6-98.el7.centos.6” package is utilized to remove from the current operating system:
$ sudo yum remove httpd-2.4.6-98.el7.centos.6
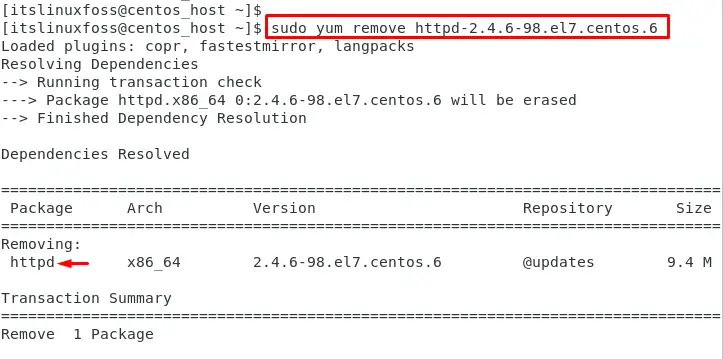
This command removes the Apache web server.
Example 2: Remove Executables, Dependencies, and Configurations
To remove the configuration files of the package, use the “autoremove” option with the “yum” command. For instance, remove the “httpd-2.4.6-98.el7.centos.6” package and its configuration files by running the following command:
$ sudo yum autoremove httpd-2.4.6-98.el7.centos.6
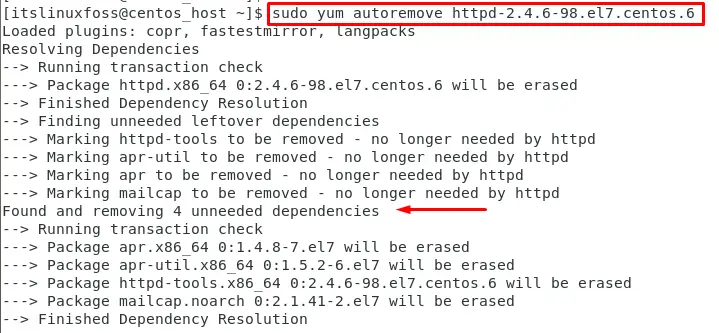
It removes the package, its dependencies, and its configuration files from the CentOS system.
How to Upgrade a Package Using YUM?
To upgrade a package using the YUM package manager, specify the package name with the “upgrade” utility. The basic syntax is provided below:
Syntax:
$ sudo yum upgrade package-name
In the above syntax, “package-name” refers to the package name that users want to upgrade.
Example 1: Upgrade Specific Package
For instance, upgrade the “bash” by specifying the package name “bash.x86_64” in the below command:
$ sudo yum upgrade bash.x86_64
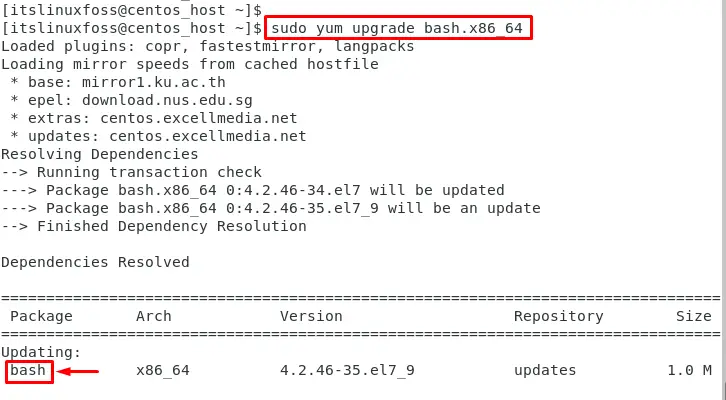
It upgrades the “bash.x86_64” to the latest version available in the repository.
Example 2: Upgrade All the Packages
To upgrade all the packages in CentOS, use the yum package manager. The yum command provides a simple way to upgrade all the installed packages on the system:
$ sudo yum upgrade
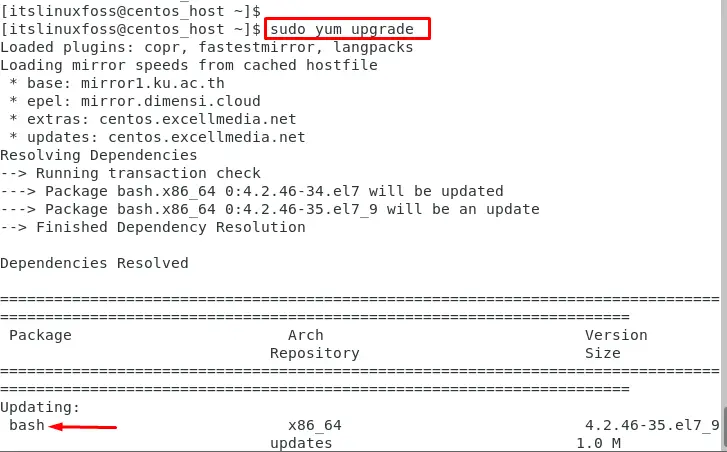
This command checks for upgrades and installs packages on the system.
Conclusion
To install, remove, and upgrade packages on CentOS, use the “yum” package manager by specifying the package name. To install, remove, and upgrade packages using YUM, execute the “sudo yum install <package-name>”, “sudo yum remove <package-name>”, and “sudo yum upgrade <package-name>” commands respectively.
This article has explained possible examples of using YUM to install, remove, and upgrade packages in CentOS.
